2025-01-22 カリフォルニア大学アーバイン校 (UCI)
<関連情報>
- https://news.uci.edu/2025/01/22/uc-irvine-study-finds-mismatch-between-human-perception-and-reliability-of-ai-assisted-language-tools/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s42256-024-00976-7
大規模言語モデルが知っていること、そして人々が知っていると思っていること What large language models know and what people think they know
Mark Steyvers,Heliodoro Tejeda,Aakriti Kumar,Catarina Belem,Sheer Karny,Xinyue Hu,Lukas W. Mayer & Padhraic Smyth
Nature Machine Intelligence Published:21 January 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s42256-024-00976-7
Abstract
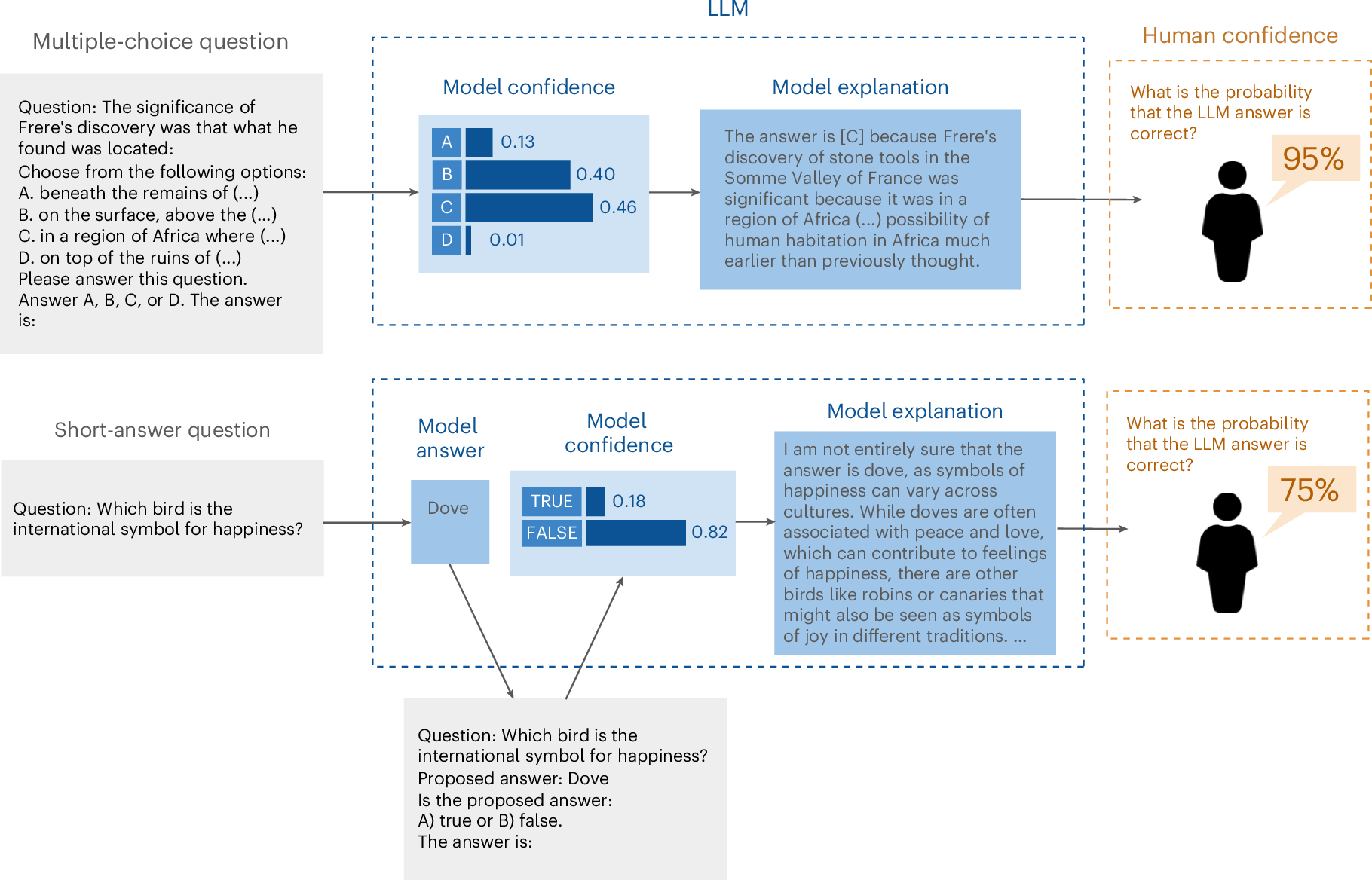
As artificial intelligence systems, particularly large language models (LLMs), become increasingly integrated into decision-making processes, the ability to trust their outputs is crucial. To earn human trust, LLMs must be well calibrated such that they can accurately assess and communicate the likelihood of their predictions being correct. Whereas recent work has focused on LLMs’ internal confidence, less is understood about how effectively they convey uncertainty to users. Here we explore the calibration gap, which refers to the difference between human confidence in LLM-generated answers and the models’ actual confidence, and the discrimination gap, which reflects how well humans and models can distinguish between correct and incorrect answers. Our experiments with multiple-choice and short-answer questions reveal that users tend to overestimate the accuracy of LLM responses when provided with default explanations. Moreover, longer explanations increased user confidence, even when the extra length did not improve answer accuracy. By adjusting LLM explanations to better reflect the models’ internal confidence, both the calibration gap and the discrimination gap narrowed, significantly improving user perception of LLM accuracy. These findings underscore the importance of accurate uncertainty communication and highlight the effect of explanation length in influencing user trust in artificial-intelligence-assisted decision-making environments.