2025-01-16 ロスアラモス国立研究所
<関連情報>
- https://www.lanl.gov/media/news/0116-ai-algorithms
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-80751-1
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-70302-z
cDVAE:粒子加速器ビーム6次元位相空間投影診断のためのVAEガイド拡散 cDVAE: VAE-guided diffusion for particle accelerator beam 6D phase space projection diagnostics
Alexander Scheinker
Scientific Report Published:26 November 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-80751-1
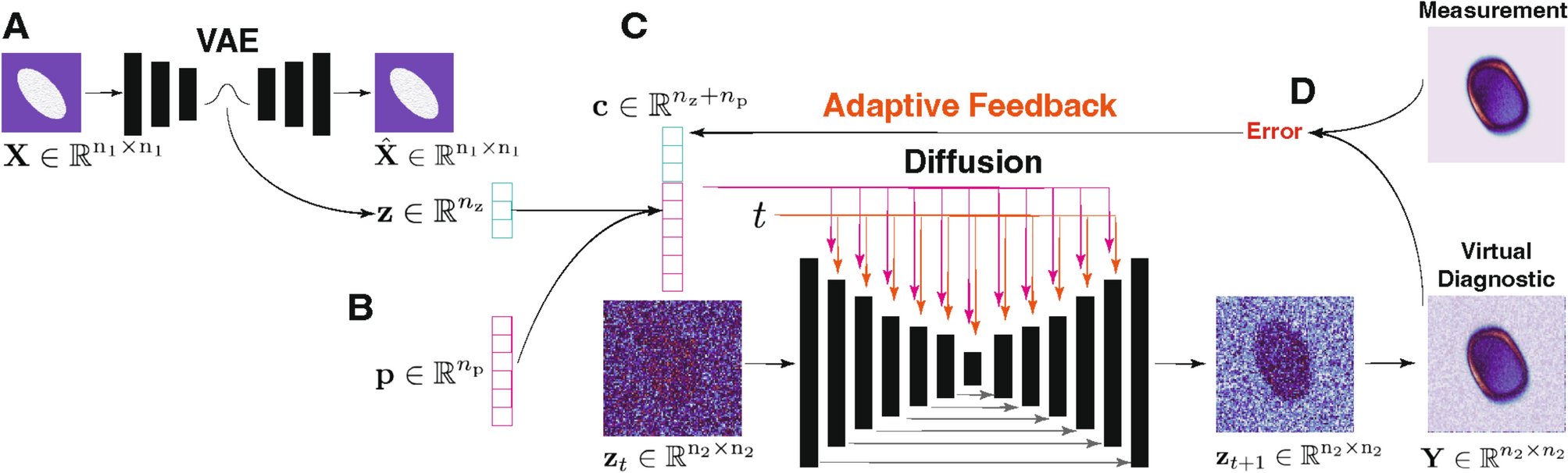
Abstract
Imaging the 6D phase space of a beam in a particle accelerator in a single shot is currently impossible. Single shot beam measurements only exist for certain 2D beam projections and these methods are destructive. A virtual diagnostic that can generate an accurate prediction of a beam’s 6D phase space would be incredibly useful for precisely controlling the beam. In this work, a generative conditional diffusion- based approach to creating a virtual diagnostic of all 15 unique 2D projections of a beam’s 6D phase space is developed. The diffusion process is guided by a combination of scalar parameters and images that are converted to low-dimensional latent vector representation by a variational autoencoder (VAE). We demonstrate that conditional diffusion guided by a VAE (cDVAE) can accurately reconstruct all 15 of the unique 2D projections of a charged particle beam’s 6D phase space for the HiRES compact accelerator.
粒子加速器ビーム診断のための条件付き誘導生成拡散 Conditional guided generative diffusion for particle accelerator beam diagnostics
Alexander Scheinker
Scientific Report Published:19 August 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-70302-z
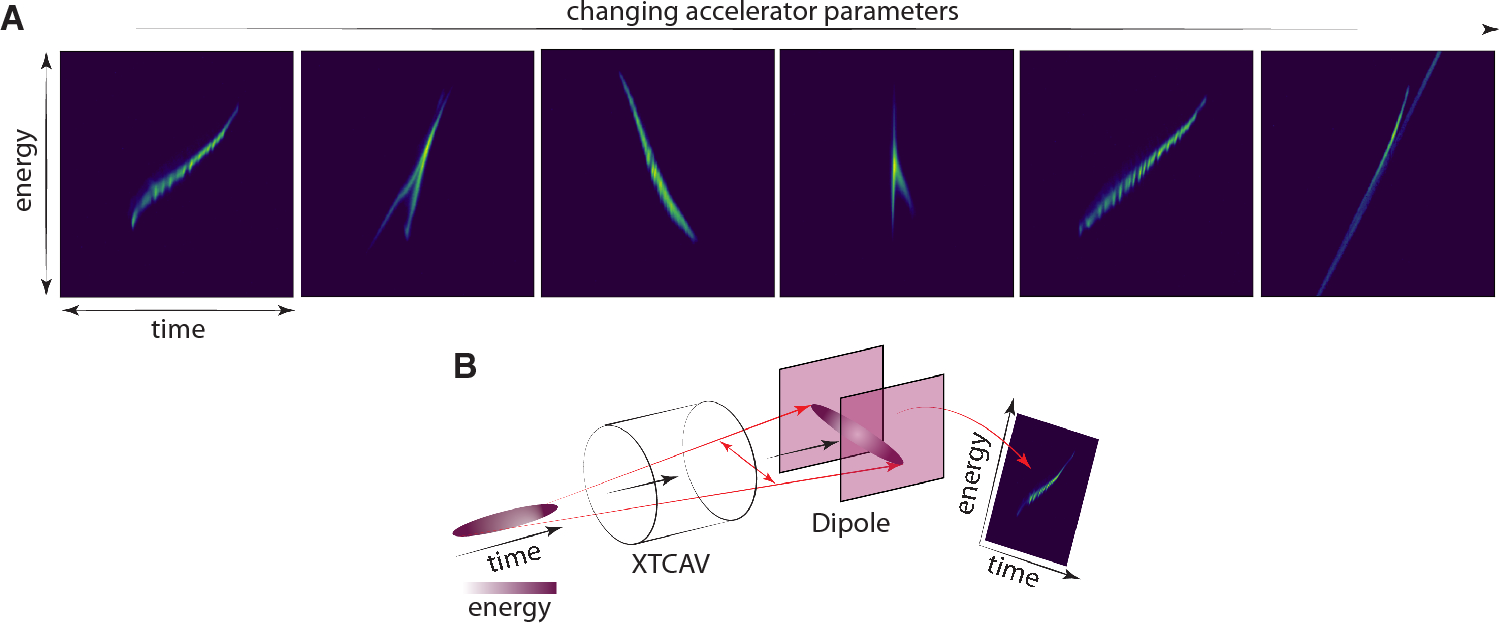
Abstract
Advanced accelerator-based light sources such as free electron lasers (FEL) accelerate highly relativistic electron beams to generate incredibly short (10s of femtoseconds) coherent flashes of light for dynamic imaging, whose brightness exceeds that of traditional synchrotron-based light sources by orders of magnitude. FEL operation requires precise control of the shape and energy of the extremely short electron bunches whose characteristics directly translate into the properties of the produced light. Control of short intense beams is difficult due to beam characteristics drifting with time and complex collective effects such as space charge and coherent synchrotron radiation. Detailed diagnostics of beam properties are therefore essential for precise beam control. Such measurements typically rely on a destructive approach based on a combination of a transverse deflecting resonant cavity followed by a dipole magnet in order to measure a beam’s 2D time vs energy longitudinal phase-space distribution. In this paper, we develop a non-invasive virtual diagnostic of an electron beam’s longitudinal phase space at megapixel resolution (1024 × 1024) based on a generative conditional diffusion model. We demonstrate the model’s generative ability on experimental data from the European X-ray FEL.