2025-01-13 ノースカロライナ州立大学 (NC State)
<関連情報>
RESQUE:持続可能なモデル再利用性のためのタスクおよび分布シフトに対する推定器の定量化 RESQUE: Quantifying Estimator to Task and Distribution Shift for Sustainable Model Reusability
Vishwesh Sangarya, Jung-Eun Kim
arXiv Submitted on 20 Dec 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2412.15511
Abstract
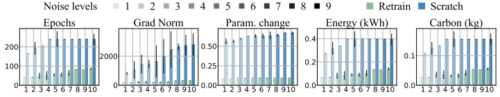
As a strategy for sustainability of deep learning, reusing an existing model by retraining it rather than training a new model from scratch is critical. In this paper, we propose REpresentation Shift QUantifying Estimator (RESQUE), a predictive quantifier to estimate the retraining cost of a model to distributional shifts or change of tasks. It provides a single concise index for an estimate of resources required for retraining the model. Through extensive experiments, we show that RESQUE has a strong correlation with various retraining measures. Our results validate that RESQUE is an effective indicator in terms of epochs, gradient norms, changes of parameter magnitude, energy, and carbon emissions. These measures align well with RESQUE for new tasks, multiple noise types, and varying noise intensities. As a result, RESQUE enables users to make informed decisions for retraining to different tasks/distribution shifts and determine the most cost-effective and sustainable option, allowing for the reuse of a model with a much smaller footprint in the environment.


