2024-09-23 ワシントン大学セントルイス校
<関連情報>
- https://source.washu.edu/2024/09/language-agents-help-large-language-models-think-better-cheaper/
- https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.03710
言語エージェントが大規模言語モデルに一般的なゼロショット推論を指示する Agent Instructs Large Language Models to be General Zero-Shot Reasoners
Nicholas Crispino, Kyle Montgomery, Fankun Zeng, Dawn Song, Chenguang Wang
arXiv last revised: 14 Aug 2024 (this version, v2)
DOI:https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2310.03710
Abstract
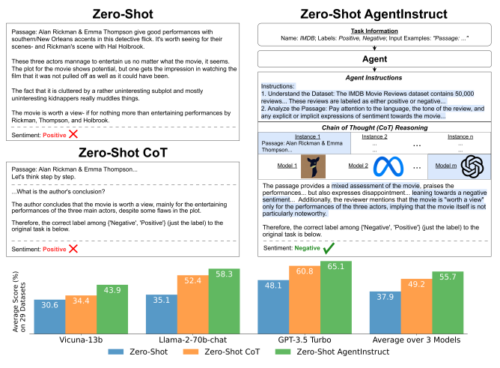
We introduce a method to improve the zero-shot reasoning abilities of large language models on general language understanding tasks. Specifically, we build an autonomous agent to instruct the reasoning process of large language models. We show this approach further unleashes the zero-shot reasoning abilities of large language models to more tasks. We study the performance of our method on a wide set of datasets spanning generation, classification, and reasoning. We show that our method generalizes to most tasks and obtains state-of-the-art zero-shot performance on 20 of the 29 datasets that we evaluate. For instance, our method boosts the performance of state-of-the-art large language models by a large margin, including Vicuna-13b (13.3%), Llama-2-70b-chat (23.2%), and GPT-3.5 Turbo (17.0%). Compared to zero-shot chain of thought, our improvement in reasoning is striking, with an average increase of 10.5%. With our method, Llama-2-70b-chat outperforms zero-shot GPT-3.5 Turbo by 10.2%.