2024-07-30 ノースカロライナ州立大学(NCState)
<関連情報>
- https://news.ncsu.edu/2024/07/researchers-develop-general-framework-for-designing-quantum-sensors/
- https://quantum-journal.org/papers/q-2024-07-30-1427/
シングルショット量子信号処理干渉計 Single-shot Quantum Signal Processing Interferometry
Jasmine Sinanan-Singh, Gabriel L. Mintzer, Isaac L. Chuang, and Yuan Liu
Quantum Published:2024-07-30
DOI:https://doi.org/10.22331/q-2024-07-30-1427
Abstract
Quantum systems of infinite dimension, such as bosonic oscillators, provide vast resources for quantum sensing. Yet, a general theory on how to manipulate such bosonic modes for sensing beyond parameter estimation is unknown. We present a general algorithmic framework, quantum signal processing interferometry (QSPI), for quantum sensing at the fundamental limits of quantum mechanics by generalizing Ramsey-type interferometry. Our QSPI sensing protocol relies on performing nonlinear polynomial transformations on the oscillator’s quadrature operators by generalizing quantum signal processing (QSP) from qubits to hybrid qubit-oscillator systems. We use our QSPI sensing framework to make efficient binary decisions on a displacement channel in the single-shot limit. Theoretical analysis suggests the sensing accuracy, given a single-shot qubit measurement, scales inversely with the sensing time or circuit depth of the algorithm. We further concatenate a series of such binary decisions to perform parameter estimation in a bit-by-bit fashion. Numerical simulations are performed to support these statements. Our QSPI protocol offers a unified framework for quantum sensing using continuous-variable bosonic systems beyond parameter estimation and establishes a promising avenue toward efficient and scalable quantum control and quantum sensing schemes beyond the NISQ era.
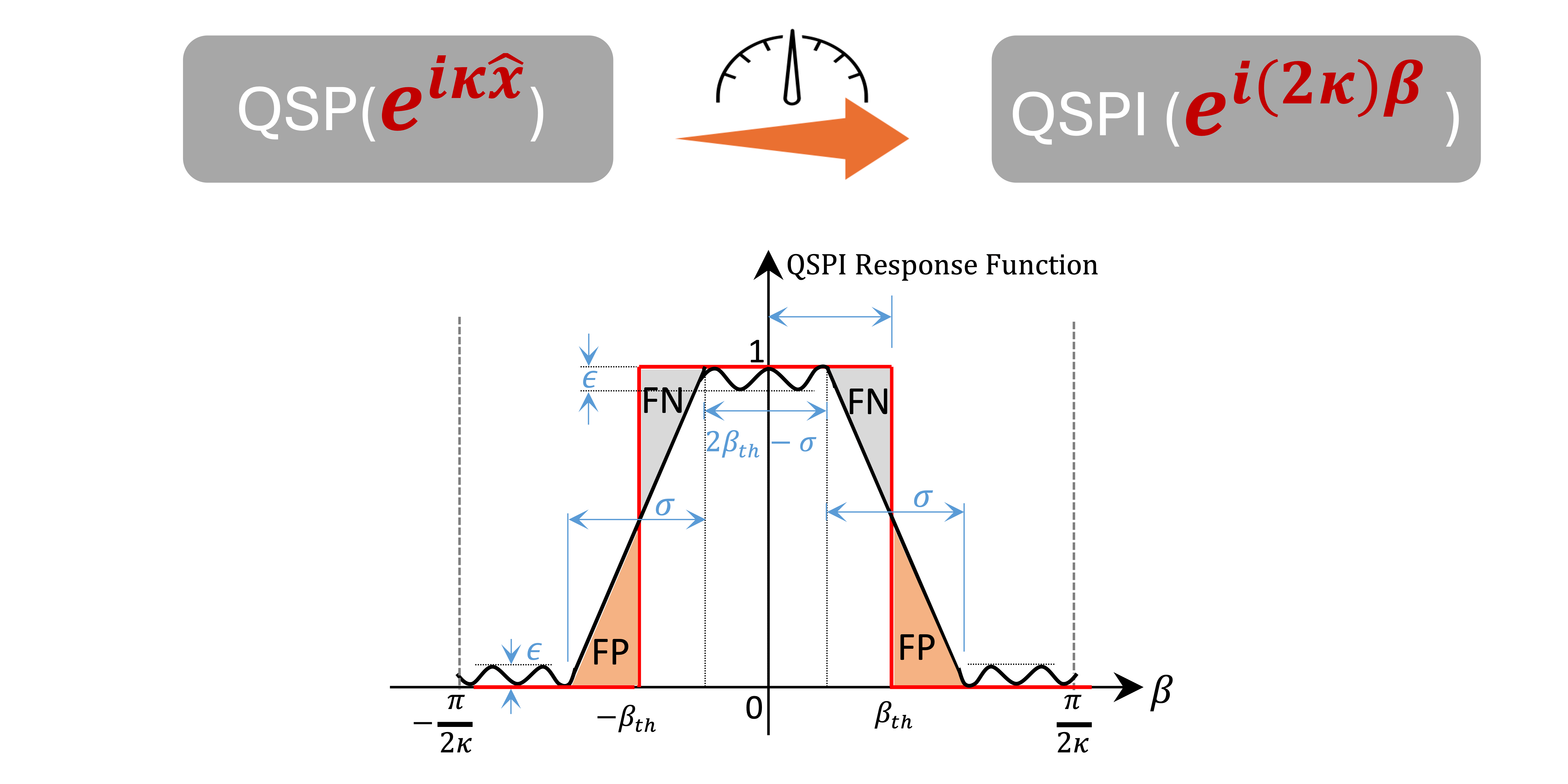
Featured image: Pictorial illustration of how in the bosonic QSP interferometry (QSPI) protocol, the qubit measurement enacts a duality between a polynomial transformation on the bosonic quadrature operators ^x<?XML:NAMESPACE PREFIX = “[default] http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML” NS = “http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML” />x^ and a polynomial transformation on the sensing parameter ββ via QSPI.
Popular summary
Quantum sensing shows promise for more powerful sensing capability that can approach the fundamental limit set by the law of quantum mechanics, but the challenge lies in being able to direct these sensors to find the signals we want. Inspired by classical signal processing filter design principles, we generalized these filter designs to quantum sensing systems, which allows us to ‘fine-tune’ an infinite dimensional quantum oscillator by coupling it to a simple two-level quantum system. Interferometry was used to encode the results into the qubit state as another nonlinear polynomial function of the underlying signal, which is then measured for readout. This novel quantum signal processing interferometry protocol allows answering binary decision problems with only a “single-shot” measurement on the qubit. These decision protocols can be chained together for quantum parameter estimation as well.
Our work provides a general theoretical framework for designing quantum sensing protocols for a variety of quantum sensors based on leading quantum hardware, including trapped ions, superconducting platform, and neutral atoms, in a fairly simple way.