2024-04-01 米国国立標準技術研究所(NIST)
<関連情報>
- https://www.nist.gov/news-events/news/2024/04/nist-researchers-use-cellphone-compass-measure-tiny-concentrations
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-47073-2
スマートフォンのコンパスを用いた液体分析物の定量的高感度測定 Quantitative, high-sensitivity measurement of liquid analytes using a smartphone compass
Mark Ferris & Gary Zabow
Nature Communications Published:30 March 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-47073-2
Abstract
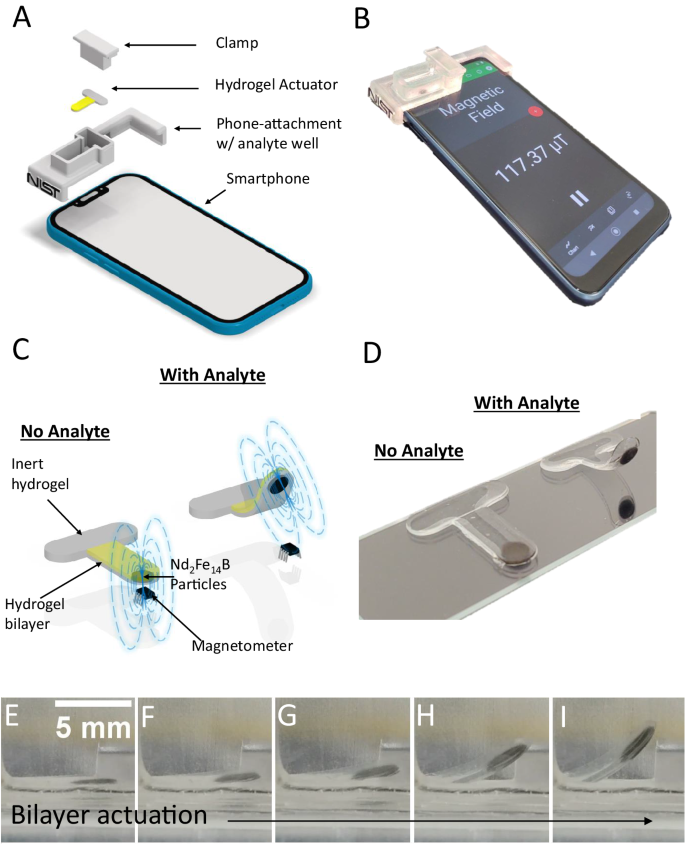
Smartphone ubiquity has led to rapid developments in portable diagnostics. While successful, such platforms are predominantly optics-based, using the smartphone camera as the sensing interface. By contrast, magnetics-based modalities exploiting the smartphone compass (magnetometer) remain unexplored, despite inherent advantages in optically opaque, scattering or auto-fluorescing samples. Here we report smartphone analyte sensing utilizing the built-in magnetometer for signal transduction via analyte-responsive magnetic-hydrogel composites. As these hydrogels dilate in response to targeted stimuli, they displace attached magnetic material relative to the phone’s magnetometer. Using a bilayer hydrogel geometry to amplify this motion allows for sensitive, optics-free, quantitative liquid-based analyte measurements that require neither any electronics nor power beyond that contained within the smartphone itself. We demonstrate this concept with glucose-specific and pH-responsive hydrogels, including glucose detection down to single-digit micromolar concentrations with potential for extension to nanomolar sensitivities. The platform is adaptable to numerous measurands, opening a path towards portable, inexpensive sensing of multiple analytes or biomarkers of interest.



