2024-02-29 テキサス大学オースチン校(UT Austin)
<関連情報>
- https://news.utexas.edu/2024/02/29/fire-resistant-sodium-battery-balances-safety-cost-and-performance/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41560-024-01469-y
安定したナトリウム金属電池のための塩による溶媒和構造の調整 Tuning the solvation structure with salts for stable sodium-metal batteries
Jiarui He,Amruth Bhargav,Laisuo Su,Julia Lamb,John Okasinski,Woochul Shin & Arumugam Manthiram
Nature Energy Published:19 February 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41560-024-01469-y
Abstract
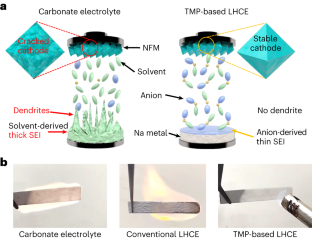
Sodium-metal batteries are an appealing, sustainable, low-cost alternative to lithium metal batteries due to the high abundance and theoretical specific capacity (1,165 mA h g−1) of sodium. However, the poor compatibility of the electrolyte with the cathode and anode leads to unstable electrode–electrolyte interphases. Here we introduce the concept of using a salt as a diluent, which enables the use of a single non-flammable solvent, such as trimethyl phosphate. By using sodium nitrate (NaNO3) salt as a model diluent, we report a 1.1 M NaFSI–NaNO3–trimethyl phosphate electrolyte that forms a stable interface with sodium-metal anode. In addition, the formation of robust cathode–electrolyte interphases on Na(Ni0.3Fe0.4Mn0.3)O2 cathode facilitates smooth phase transitions, thus leading to stable cycle life with a capacity retention of 80% over 500 cycles at C/5 rate in Na||Na(Ni0.3Fe0.4Mn0.3)O2 cells. The work demonstrates a promising approach towards the development of safe, low-cost, sustainable high-performance sodium-metal batteries.



