2023-10-26 ドイツ連邦共和国・ミュンヘン工科大学(TUM)
・ TUM、Bosch およびフラウンホーファー・フォトニック・マイクロシステム研究所(IPMS)が、既存のインメモリーコンピューティングアプローチの 2 倍の性能を有する、強誘電性電界効果トランジスタ(FeFETs)を利用した AI チップを開発。
・ 僅か 28nm の FeFETs が数百万個搭載される新 AI チップでは、従来では演算のみを実行するトランジスタがデータの記憶場所も兼ねることで、高速化と省エネ化に加え高性能化を実現。FeFETs は電圧が加わると分極する特性の電気的なスイッチで、電源オフ後もデータを保持できる。
・ また、例えば飛行中のドローンのリアルタイム演算のようなアプリケーションで重要となる、発熱の速度も減速させる。このようなタスクは極めて複雑で、コンピューターはエネルギーを大量に消費する。
・ 米国企業グローバルファウンドリーズの協力で製造されたこの新 AI チップでは、885TOPS/W(消費電力 1W あたりの演算回数)を達成。Samsung の MRAM チップを含む他の AI チップの 2 倍の性能(一般的な CMOS チップは 10~20TOPS/W 程度)。
・ 最終的な目標は、新 AI チップを深層学習(DL)アルゴリズムで使用し、オブジェクトの認識や飛行中のドローンからのタイムラグのないデータ処理だが、これらの実現は早くて 3~5 年先となると予想。実用化には対象分野の特定の基準を満たす必要があり、コンピューターサイエンス、情報学、電気工学等の多様な分野の研究者との学際的な協力が鍵となる。
・ 本研究には、EU Horizon 2020 研究開発プログラムおよびベルギー、フランス、ドイツ、ポルトガル、スペイン、オランダ、スイスが支援する、電子部品とシステムの共同技術イニシアティブ (ECSEL Joint
Undertaking (JU) )が資金を提供した。
URL: https://www.tum.de/en/news-and-events/all-news/press-releases/details/tum-professor-develops-an-energy-saving-ai-chip
<NEDO海外技術情報より>
関連情報
Nature Communications 掲載論文(フルテキスト)
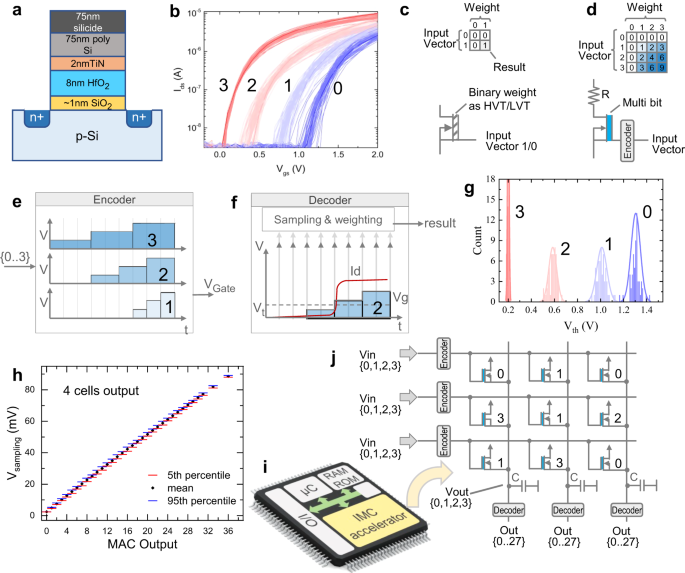
First demonstration of in-memory computing crossbar using multi-level Cell FeFET
URL: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-42110-y
Abstract
Advancements in AI led to the emergence of in-memory-computing architectures as a promising solution for the associated computing and memory challenges. This study introduces a novel in-memory-computing (IMC) crossbar macro utilizing a multi-level ferroelectric field-effect transistor (FeFET) cell for multi-bit multiply and accumulate (MAC) operations. The proposed 1FeFET-1R cell design stores multi-bit information while minimizing device variability effects on accuracy. Experimental validation was performed using 28 nm HKMG technology-based FeFET devices. Unlike traditional resistive memory-based analog computing, our approach leverages the electrical characteristics of stored data within the memory cell to derive MAC operation results encoded in activation time and accumulated current. Remarkably, our design achieves 96.6% accuracy for handwriting recognition and 91.5% accuracy for image classification without extra training. Furthermore, it demonstrates exceptional performance, achieving 885.4 TOPS/W–nearly double that of existing designs. This study represents the first successful implementation of an in-memory macro using a multi-state FeFET cell for complete MAC operations, preserving crossbar density without additional structural overhead.



