2023-09-13 マサチューセッツ工科大学(MIT)
◆新しい手法により、リチウム鉄リン酸塩ナノ粒子の異なる領域でのリチウム挿入反応速度の変動など、以前には見ることができなかった現象が明らかになりました。
◆最も重要な実用的な発見は、これらの反応速度の変動が粒子表面の炭素コーティングの厚さの違いと関連していることであり、これは充電および放電の効率向上につながる可能性があります。
<関連情報>
- https://news.mit.edu/2023/pixel-analysis-yields-insights-lithium-ion-batteries-0913
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06393-x
X線動画から不均一反応速度をピクセル単位で学習 Learning heterogeneous reaction kinetics from X-ray videos pixel by pixel
Hongbo Zhao,Haitao Dean Deng,Alexander E. Cohen,Jongwoo Lim,Yiyang Li,Dimitrios Fraggedakis,Benben Jiang,Brian D. Storey,William C. Chueh,Richard D. Braatz & Martin Z. Bazant
Nature Published:13 September 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-06393-x
Abstract
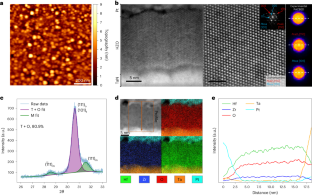
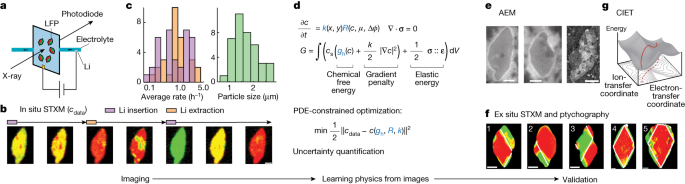
Reaction rates at spatially heterogeneous, unstable interfaces are notoriously difficult to quantify, yet are essential in engineering many chemical systems, such as batteries1 and electrocatalysts2. Experimental characterizations of such materials by operando microscopy produce rich image datasets3,4,5,6, but data-driven methods to learn physics from these images are still lacking because of the complex coupling of reaction kinetics, surface chemistry and phase separation7. Here we show that heterogeneous reaction kinetics can be learned from in situ scanning transmission X-ray microscopy (STXM) images of carbon-coated lithium iron phosphate (LFP) nanoparticles. Combining a large dataset of STXM images with a thermodynamically consistent electrochemical phase-field model, partial differential equation (PDE)-constrained optimization and uncertainty quantification, we extract the free-energy landscape and reaction kinetics and verify their consistency with theoretical models. We also simultaneously learn the spatial heterogeneity of the reaction rate, which closely matches the carbon-coating thickness profiles obtained through Auger electron microscopy (AEM). Across 180,000 image pixels, the mean discrepancy with the learned model is remarkably small (<7%) and comparable with experimental noise. Our results open the possibility of learning nonequilibrium material properties beyond the reach of traditional experimental methods and offer a new non-destructive technique for characterizing and optimizing heterogeneous reactive surfaces.