2023-08-29 オランダ・デルフト工科大学(TUDelft)
◆研究者たちは、Quantum dotsのアドレッシングに関する新しい方法を開発し、多くのキュービットを効率的に操作できるようにしました。このアプローチは、Quantum computerのスケーリングアップに大きな利点をもたらし、量子コンピュータの発展に向けた重要な進歩です。また、キュービットの品質も向上し、高い忠実度で動作することが示されています。
◆これらの進歩は、将来的には百万のキュービットが必要とされる量子コンピュータに向けた重要なステップです。また、量子ドットシステムは、量子シミュレーションにおいて非常に効果的であることが示唆されており、物理学の重要な質問に答えるための新たな道を開いています。
<関連情報>
- https://www.tudelft.nl/en/2023/tu-delft/chessboard-like-operation-of-worlds-largest-controllable-quantum-dot-array
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41565-023-01491-3
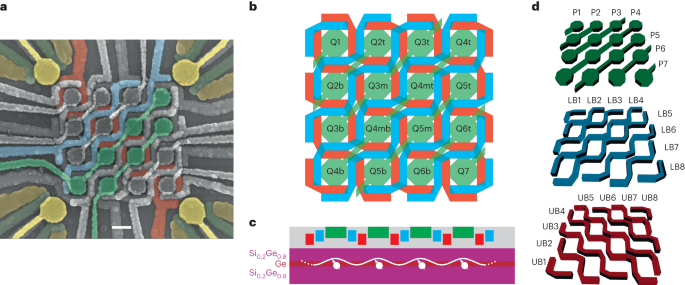
16個の半導体量子ドットクロスバーアレイを共有制御 Shared control of a 16 semiconductor quantum dot crossbar array
Francesco Borsoi,Nico W. Hendrickx,Valentin John,Marcel Meyer,Sayr Motz,Floor van Riggelen,Amir Sammak,Sander L. de Snoo,Giordano Scappucci & Menno Veldhorst
Nature Nanotechnology Published:28 August 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-023-01491-3
Abstract
The efficient control of a large number of qubits is one of the most challenging aspects for practical quantum computing. Current approaches in solid-state quantum technology are based on brute-force methods, where each and every qubit requires at least one unique control line—an approach that will become unsustainable when scaling to the required millions of qubits. Here, inspired by random-access architectures in classical electronics, we introduce the shared control of semiconductor quantum dots to efficiently operate a two-dimensional crossbar array in planar germanium. We tune the entire array, comprising 16 quantum dots, to the few-hole regime. We then confine an odd number of holes in each site to isolate an unpaired spin per dot. Moving forward, we demonstrate on a vertical and a horizontal double quantum dot a method for the selective control of the interdot coupling and achieve a tunnel coupling tunability over more than 10 GHz. The operation of a quantum electronic device with fewer control terminals than tunable experimental parameters represents a compelling step forward in the construction of scalable quantum technology.