2023-09-06 マサチューセッツ工科大学(MIT)
◆研究者たちは、バッテリー不要のシステムの通信範囲を拡大することで、養殖業、沿岸のハリケーン予測、気候変動モデリングなどの応用をより実現可能にしました。彼らのシステムは、音波にデータを符号化して通信し、これを反射または散乱させています。新たな設計と数学モデルにより、通信範囲が大幅に拡大され、数キロメートル単位の距離で通信できる可能性が示唆されています。
<関連情報>
- https://news.mit.edu/2023/devices-offers-battery-free-underwater-communication-0906
- https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3603269.3604814
- http://www.mit.edu/~fadel/papers/PAB-theory-paper.pdf
ヴァン・アッタ音響ネットワークにより長距離水中後方散乱を可能にする Enabling Long-Range Underwater Backscatter via Van Atta Acoustic Networks
Aline Eid,Jack Rademacher,Waleed Akbar,Purui Wang,Ahmed Allam,Fadel Adib
ACM SIGCOMM Published:01 September 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1145/3603269.3604814
ABSTRACT
We present the design, implementation, and evaluation of Van Atta Acoustic Backscatter (VAB), a technology that enables long-range, ultra-low-power networking in underwater environments. At the core of VAB is a novel, scalable underwater backscatter architecture that bridges recent advances in RF backscatter (Van Atta architectures) with ultra-low-power underwater acoustic networks. Our design introduces multiple innovations across the networking stack, which enable it to overcome unique challenges that arise from the electro-mechanical properties of underwater backscatter and the challenging nature of low-power underwater acoustic channels. We implemented our design in an end-to-end system, and evaluated it in over 1,500 real-world experimental trials in a river and the ocean. Our evaluation in stationary setups demonstrates that VAB achieves a communication range that exceeds 300m in round trip backscatter across orientations (at BER of 10−3). We compared our design head-to-head with past state-of-the-art systems, demonstrating a 15× improvement in communication range at the same throughput and power. By realizing hundreds of meters of range in underwater backscatter, this paper presents the first practical system capable of coastal monitoring applications. Finally, our evaluation represents the first experimental validation of underwater backscatter in the ocean.
水中後方散乱チャネル:理論、リンクバジェット、実験的検証 The Underwater Backscatter Channel: Theory, Link Budget, and Experimental Validation
Waleed Akbar,Ahmed Allam,Fadel Adib
ACM MobiCom
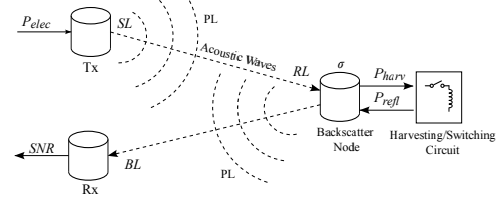
ABSTRACT
Underwater backscatter is a recent networking technology that enables net-zero-power communication and sensing in underwater environments. Existing research on underwater backscatter has focused on designing and demonstrating early systems with impressive capabilities; however, what remains critically missing is an end-to-end analysis of the underwater backscatter communication channel, which is necessary to understand the potential of this technology to scale to real-world applications and practical deployments. This paper presents the first comprehensive theoretical and empirical analysis of the underwater backscatter channel, including the downlink and uplink of end-to-end backscatter. We introduce a closed-form analytical model that encompasses the physical properties of piezoelectric materials, electromechanical coupling, electrical impedance, and the underwater acoustic channel. We verify the correctness of this theoretical analysis through both finite-element-model physical simulations and real-world experimental validation in a river, demonstrating that the analytical model matches our real-world experiments with a median deviation of only 0.76 dB. Using this model, we then simulate the theoretical limits of underwater backscatter as a function of different design parameters and identify pathways for pushing underwater backscatter toward its theoretical limits.



