2023-05-18 レンセラー工科大学 (RPI)
◆この研究は、材料科学の分野において重要な突破口であり、半導体、太陽電池、電気自動車技術などへの応用の可能性が示されました。研究チームの発見は、新しい特性を持つ材料の開発につながると期待されています。
<関連情報>
- https://news.rpi.edu/content/2023/05/18/rensselaer-researcher-transforms-our-understanding-crystals
- https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2023/SM/D3SM00199G
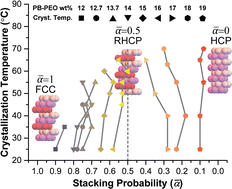
コロイド結晶が安定なランダム秩序を経て連続的に転移することを発見 Continuous transition of colloidal crystals through stable random orders
Juhong Ahn,Liwen Chen,Patrick T. Underhill,Guillaume Freychet,Mikhail Zhernenkov and Sangwoo Lee
Soft Matter Published:14 Apr 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1039/D3SM00199G
Abstract
Randomly stacked 2D hexagonal close-packed (RHCP) layer structures are frequently observed in colloids and other material systems but are considered metastable. We report a stable RHCP phase domain of poly(butadiene-b-ethylene oxide) (PB-PEO) diblock copolymer micellar colloids in water. The stable RHCP colloidal crystals emerge in the middle of a continuously transiting phase domain of close-packed PB-PEO colloids from a face-centered cubic (FCC) polytype to a HCP polytype. We attribute the stability of RHCP structures to two competing contributions, entropic preference for FCC lattices and long PEO corona chains stabilizing HCP lattices. When these two contributions become comparable in the phase space, thermal fluctuation randomizes the stacking order of the 2D-HCP layers, and RHCP orders are stabilized. The continuously transiting close-packed structures of PB-PEO colloids with stable RHCP states suggest that similar structural transitions and equivalent RHCP states may occur in other polytypic crystal systems because polytypic crystals have the common crystal construction rule, i.e., stacking 2D-HCP lattice layer groups in different orders.