2023-03-15 ペンシルベニア州立大学(PennState)
YSEは、毎日1,500平方度の空を調査し、天文学的現象を発見することを目的としており、これまでに2,000以上の超新星が発見された。
この調査は、天文学における重要なマイルストーンとなると同時に、未知の宇宙現象を発見するためにAIと機械学習技術が活用された。
また、Vera C. Rubin Observatory Legacy Survey of Space and Timeという計画中の10年間の調査に向けた事前の準備としても活用される予定だ。
<関連情報>
- https://www.psu.edu/news/eberly-college-science/story/thousands-new-cosmic-explosions-discovered-young-supernova-experiment/
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/2211.07128.pdf
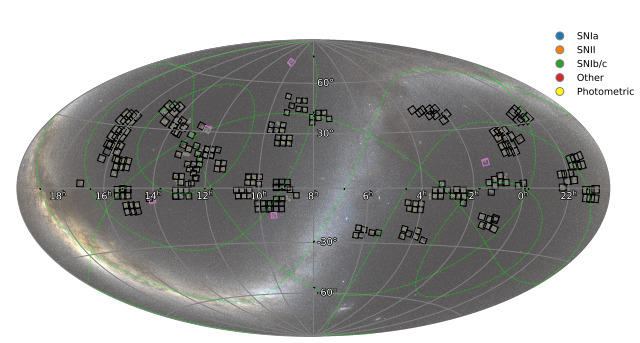
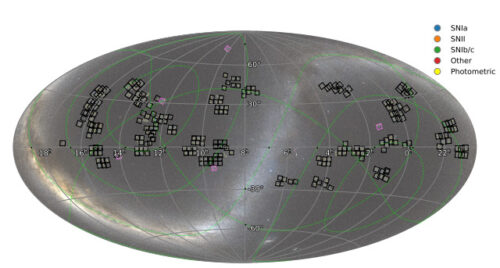
ヤング超新星実験データリリース1(YSE DR1):光度曲線と測光1975年の超新星の分類 The Young Supernova Experiment Data Release 1 (YSE DR1): Light Curves and Photometric Classification of 1975 Supernovae
P.D.Aleo,K.Malanchev,S.Sharief,D.O.Jones,G.Narayan,R.J.Foley,V.A.Villar,C.R.Angus,V.F.Baldassare,M.J.Bustamante.Rosell,D.Chatterjee,C.Cold,D.A.Coulter,K.W.Davis,S.Dhawan,M.R.Drout,A.Engel,K.D.French,A.Gagliano,C.Gall,J.Hjorth,M.E.Huber,W.V.Jacobson.Galan,C.D.Kilpatrick,D.Langeroodi,P.Macias,K.S.Mandel,R.Margutti,F.Matasic,P.McGill,J.D.R.Pierel,E.Ramirez.Ruiz,C.L.Ransome,C.Rojas.Bravo,M.R.Siebert,K.W.Smith,K.M.deSoto,M.C.Stroh,S.Tinyanont,K.Taggart,S.M.Ward,R.Wojtak,K.Auchettl,P.K.Blanchard,T.J.L.deBoer,B.M.Boyd,C.M.Carroll,K.C.Chambers,L.DeMarchi,G.Dimitriadis,S.A.Dodd,N.Earl,D.Farias,H.Gao,S.Gomez,M.Grayling,C.Grillo,E.E.Hayes,T.Hung,L.Izzo,N.Khetan,A.N.Kolborg,J.A.P.LawSmith,N.LeBaron,C.C.Lin,Y.Luo,E.A.Magnier,D.Matthews,B.Mockler,A.J.G.O’Grady,Y.C.Pan,C.A.Politsch,S.I.Raimundo,A.Rest,R.Ridden.Harper,A.Sarangi,S.L.Schrøder,S.J.Smartt,G.Terreran,S.Thorp,J.Vazquez,R.J.Wainscoat,Q.Wang,A.R.Wasserman,S.K.Yadavalli,R.Yarza,Y.Zenati,
arxiv Accepted:2023February10
ABSTRACT
We present the Young Supernova Experiment Data Release 1 (YSE DR1), comprised of processed multi-color Pan-STARRS1 (PS1) griz and Zwicky Transient Facility (ZTF) gr photometry of 1975 transients with host-galaxy associations, redshifts, spectroscopic/photometric classifications, and additional data products from 2019 November 24 to 2021 December 20. YSE DR1 spans discoveries and observations from young and fast-rising supernovae (SNe) to transients that persist for over a year, with a redshift distribution reaching z ≈ 0.5. We present relative SN rates from YSE’s magnitudeand volume-limited surveys, which are consistent with previously published values within estimated uncertainties for untargeted surveys. We combine YSE and ZTF data, and create multi-survey SN simulations to train the ParSNIP and SuperRAENN photometric classification algorithms; when validating our ParSNIP classifier on 472 spectroscopically classified YSE DR1 SNe, we achieve 82% accuracy across three SN classes (SNe Ia, II, Ib/Ic) and 90% accuracy across two SN classes (SNe Ia, core-collapse SNe). Our classifier performs particularly well on SNe Ia, with high (>90%) individual completeness and purity, which will help build an anchor photometric SNe Ia sample for cosmology. We then use our photometric classifier to characterize our photometric sample of 1483 SNe, labeling 1048 (∼71%) SNe Ia, 339 (∼23%) SNe II, and 96 (∼6%) SNe Ib/Ic. YSE DR1 provides a training ground for building discovery, anomaly detection, and classification algorithms, performing cosmological analyses, understanding the nature of red and rare transients, exploring tidal disruption events and nuclear variability, and preparing for the forthcoming Vera C. Rubin Observatory Legacy Survey of Space and Time.