2022-03-14 アメリカ・ローレンスリバモア国立研究所(LLNL)
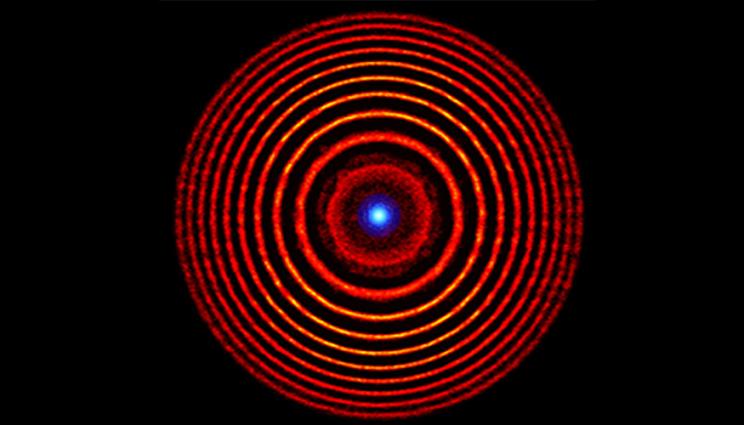
Colorized illustration from a simulation of a holographic plasma lens. The red concentric circles denote alternating high- and low-density plasma rings. The blue dot at the center represents the focused light. Image by Matthew Edwards/LLNL.
- <関連情報>
- https://www.llnl.gov/news/holographic-plasma-lenses-ultra-high-power-lasers
- https://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.128.065003
ホログラフィックプラズマレンズ Holographic Plasma Lenses
Phys. Rev. Lett. 128, 065003 – Published 8 February 2022
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.128.065003 © 2022 American Physical Society
ABSTRACT
A hologram fully encodes a three-dimensional light field by imprinting the interference between the field and a reference beam in a recording medium. Here we show that two collinear pump lasers with different foci overlapped in a gas jet produce a holographic plasma lens capable of focusing or collimating a probe laser at intensities several orders-of-magnitude higher than the limits of a nonionized optic. We outline the theory of these diffractive plasma lenses and present simulations for two plasma mechanisms that allow their construction: spatially varying ionization and ponderomotively driven ion-density fluctuations. Damage-resistant plasma optics are necessary for manipulating high-intensity light, and divergence control of high-intensity pulses—provided by holographic plasma lenses—will be a critical component of high-power plasma-based lasers.



