(Black Phosphorous Tunnel Field-Effect Transistor as an Alternative Ultra-low Power Switch)
2020/2/21 大韓民国・KAIST(旧・韓国科学技術院)
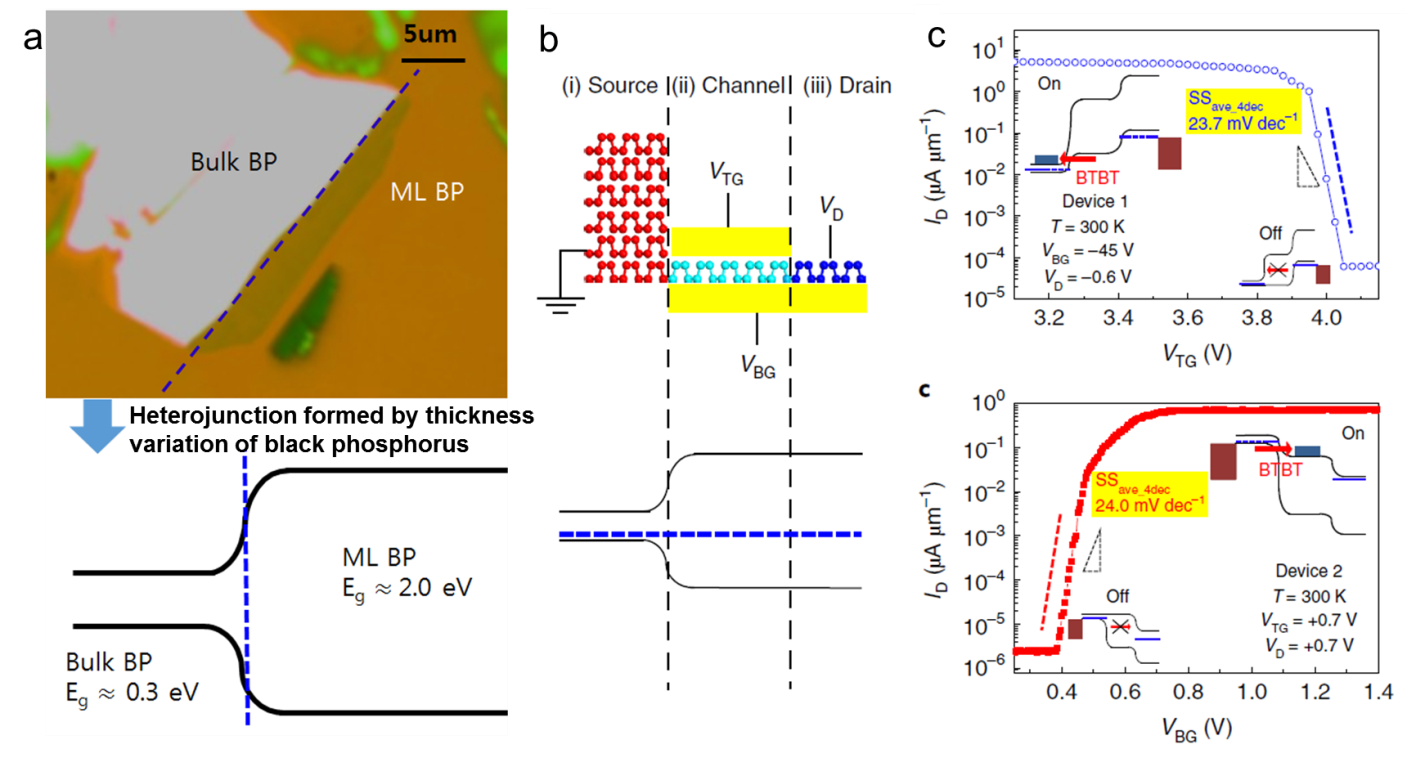
・ KAIST が、黒リンを使用した高速・低電力のヘテロ接合の電界効果トランジスタ(TFET)を開発。
・ 黒リン層の薄さを調整することで、オン電流を低減させていたヘテロ接合のインターフェースの課題を克服。
・ 新トランジスタは、従来の相補型金属酸化物半導体(CMOS)トランジスタに比して、スイッチング電力とスタンバイ電力消費量がそれぞれ1/10と1/10000。過去最小のサブスレッショルドスイング値(S値)と過去最大のオン電流を達成。CMOS トランジスタに匹敵する作動速度をより少ない電力消費で実現する。
・ トランジスタの微細化は、インフォメーション・テクノロジー(IT)の進展の鍵。増大する電力消費量によりムーアの法則の限界が近づく中、代替となる新しいトランジスタの開発は喫緊の課題となっている。
・ CMOS トランジスタのスイッチングとスタンバイ電力を低減するには、S 値の低減が必須だが、CMOS トランジスタではサブスレッショルドスイング値の下限が 60mV/dec となっている。
・ 一方、量子トンネル効果を利用する TFET では、そのような CMOS の S 値の下限を下回ることも可能なため、CMOS トランジスタの代替として期待されている。特に、ヘテロ接合による TEFT はより低いS 値と高いオン電流を提供する。
・ 本研究には、韓国研究財団(NRF)が資金を提供した。
URL: https://news.kaist.ac.kr/newsen/html/news/?mode=V&mng_no=5490&skey=category&sval=re
search&list_s_date=&list_e_date=&GotoPage=1
(関連情報)
Nature Nanotechnology 掲載論文(アブストラクトのみ:全文は有料)
Thickness-controlled black phosphorus tunnel field-effect transistor for low-power switches
URL: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41565-019-0623-7
<NEDO海外技術情報より>
Abstract
The continuous down-scaling of transistors has been the key to the successful development of current information technology. However, with Moore’s law reaching its limits, the development of alternative transistor architectures is urgently needed1. Transistors require a switching voltage of at least 60 mV for each tenfold increase in current, that is, a subthreshold swing (SS) of 60 mV per decade (dec). Alternative tunnel field-effect transistors (TFETs) are widely studied to achieve a sub-thermionic SS and high I60 (the current where SS becomes 60 mV dec–1)2. Heterojunction (HJ) TFETs show promise for delivering a high I60, but experimental results do not meet theoretical expectations due to interface problems in the HJs constructed from different materials. Here, we report a natural HJ-TFET with spatially varying layer thickness in black phosphorus without interface problems. We have achieved record-low average SS values over 4–5 dec of current (SSave_4dec ~22.9 mV dec–1 and SSave_5dec ~26.0 mV dec–1) with record-high I60 (I60 = 0.65–1 μA μm–1), paving the way for application in low-power switches.



