(Scientists led by NTU Singapore identify new catalysts for more efficient water splitting)
2020/8/3 シンガポール・南洋(ナンヤン)理工大学(NTU)
・ NTU が率いる研究チーム(北京と香港の各研究所、シンガポール科学技術研究庁(A★STAR)およびNTUの科学者らで構成)が、低コストの電解触媒であるスピネル酸化物に関する重要な発見と進展を報告。
・ 水電解による水素ガス生成プロセスにおける主要な課題は、水素生成コストを上昇させる、水電解化学反応でのエネルギーの損失。
・ 水電解プロセスでは、2 種類の化学反応でそれぞれ水素と酸素が生成され、各ガスは電解槽のメンブレンで分離される。酸素発生反応(OER)は効率的な水電解による水素生成に不可欠なものだが、化学反応速度が緩慢で全体のエネルギー変換効率を低下させる。そのため、金属酸化物等の触媒で反応速度を上げる必要がある。
・ 貴金属酸化物は、エネルギー消費を抑えてエネルギー変換効率を向上させる最高水準の触媒であるが、資源量の制約、高コストや耐久性の低さが大規模なアプリケーションを制限している。
・ 安価な遷移金属のスピネル酸化物は、このような課題を解決する安定した低コスト触媒として注目を集めているが、その働きが理解されていなかった。
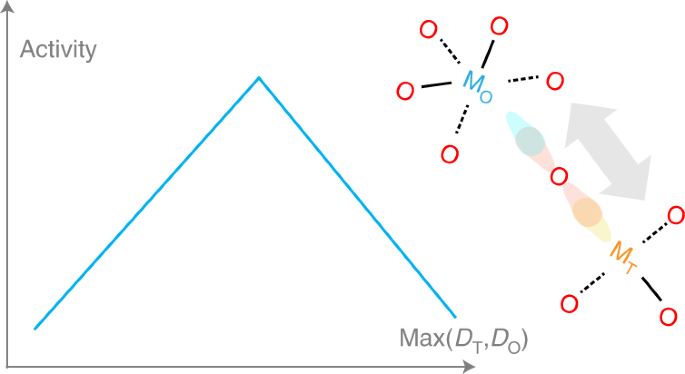
・ 今回、スピネル酸化物が水電解を加速させるメカニズムを原子レベルで解明。さらに、この発見を基に 300 種類を超えるスピネル酸化物のデータセットで機械学習モデルを訓練し、同材料によるあらゆる触媒の効率性を瞬時に予測。
・ 触媒活性を高めて水電解の効率性を向上させるスピネル酸化物として、マンガンとアルミニウムから成る酸化物を特定し、これを作製・実証した。これらの結果は、水電解による水素ガスの大規模製造の実現をさらに近づけるもの。
・ シンガポールでは、2050 年までに温暖化ガス排出量を半減する目標に向け、同国のエネルギー市場監督庁(EMA)が水素ガスの利用をカーボンフットプリント削減の一手段としている。
・ 今回作製した新触媒の普及には、長期間の水素生成を支えるための、アルカリ電解槽のメンブレンの改良と産業レベルでの機能性の確認が必要となる。
・ 本研究には、シンガポール教育省(MOE)とシンガポール国立研究財団(NRF)が資金を提供した。
URL: https://media.ntu.edu.sg/NewsReleases/Pages/newsdetail.aspx?news=530ebde8-41e4-
4c37-a6ac-8401d649dce9
<NEDO海外技術情報より>
(関連情報)
Nature Catalysis 掲載論文(アブストラクトのみ:全文は有料)
Covalency competition dominates the water oxidation structure–activity relationship on spinel oxides
URL: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41929-020-0465-6
Abstract
Spinel oxides have attracted growing interest over the years for catalysing the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) due to their efficiency and cost-effectiveness, but fundamental understanding of their structure–property relationships remains elusive. Here we demonstrate that the OER activity on spinel oxides is intrinsically dominated by the covalency competition between tetrahedral and octahedral sites. The competition fabricates an asymmetric MT−O−MO backbone where the bond with weaker metal–oxygen covalency determines the exposure of cation sites and therefore the activity. Driven by this finding, a dataset with more than 300 spinel oxides is computed and used to train a machine-learning model for screening the covalency competition in spinel oxides, with a mean absolute error of 0.05 eV. [Mn]T[Al0.5Mn1.5]OO4 is predicted to be a highly active OER catalyst and subsequent experimental results confirm its superior activity. This work sets mechanistic principles of spinel oxides for water oxidation, which may be extendable to other applications.