2025-11-11 中国科学院(CAS)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/tech/202511/t20251113_1115117.shtml
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41378-025-01022-1
デュアルモード動作方式を用いた差動MEMS共振加速度計における温度ドリフト抑制と測定デッドゾーンの排除 Temperature drift suppression and measurement dead zone elimination in differential MEMS resonant accelerometers using dual-mode operating method
Bingchen Zhu,Zheng Wang,Liangbo Ma,Zhaoyang Zhai,Kunfeng Wang,Wuhao Yang,Xiaorui Bie & Xudong Zou
Microsystems Nanoengineering Published:28 October 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41378-025-01022-1
Abstract
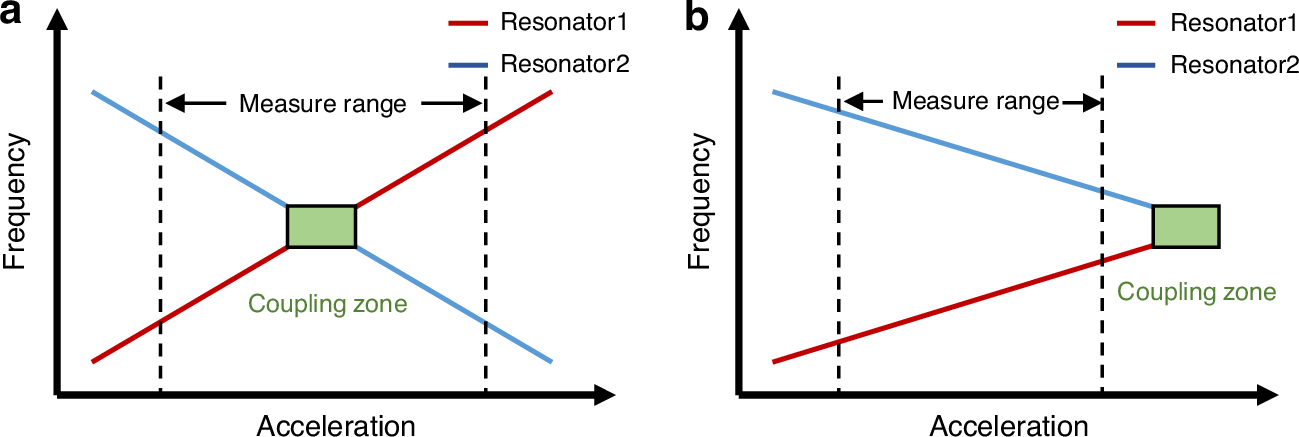
This paper proposes a differential mode measurement and control system (DMCS) for differential MEMS resonant accelerometer (DMRA), which operates the differential resonators of the DMRA at different vibration modes. Unlike traditional DMRA, the first resonator of the differential resonator operates in the first-order mode (R1M1), and the second resonator operates in the second-order mode (R2M2). Within the measurement range of DMRA, the frequencies of the two resonators will not cross, so there will be no mutual interference. This ensures the structural symmetry of the DMRA while avoiding the measurement dead zone phenomenon caused by the coupling of the differential vibration beam at similar resonant frequencies. The structural symmetry of the differential resonator ensures good temperature consistency of the differential vibration beam, and the consistency of the temperature frequency coefficient matches well, which enables the differential resonator to strongly suppress the temperature-induced common-mode effects. During the temperature cycling process between -20 °C and 80 °C, the equivalent acceleration drift of R1M1 and R2M2 were 341.6 mg and 414.6 mg, respectively. After using the differential temperature compensation algorithm, the equivalent acceleration drift was reduced to 1.19 mg. The minimum Allan variance measured statically at room temperature decreased from 1.42 μg@0.85 s for R1M1 and 1.52 μg@0.85 s for R2M2 to 0.23 μg@7.15 s, indicating a significant improvement in the long-term stability of DMRA. In addition, the differential measuring method also eliminated common mode ambient noise in low frequency range, ultimately achieving a noise level of 220 ng/√Hz@(0.2–0.8 Hz) for a prototype device with a measurement range exceeding ±5 g.



