2025-10-24 中国科学院(CAS)
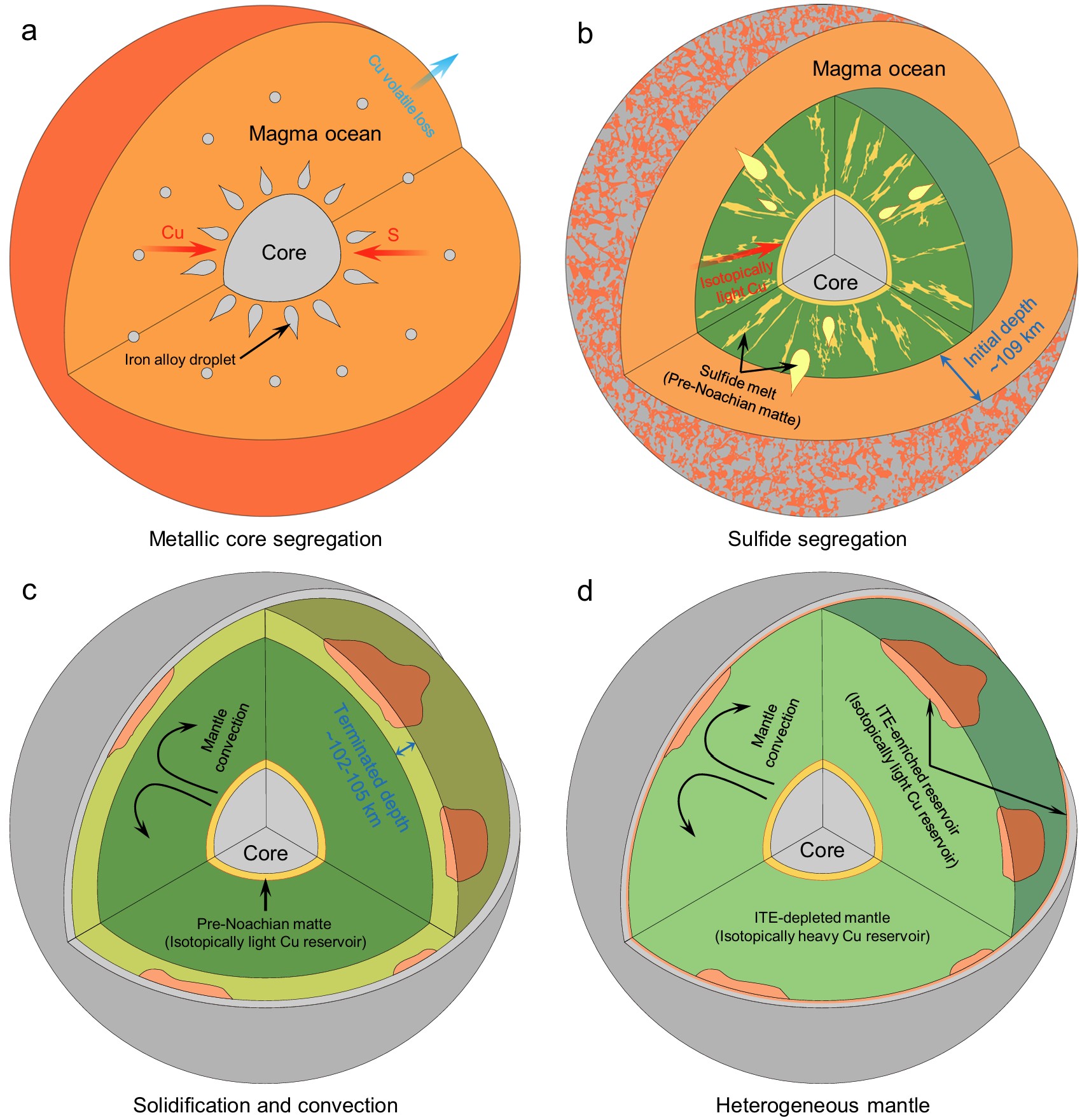
Schematic diagram of martian magma ocean evolution. (Image by IGCAS)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/earth/202510/t20251024_1094799.shtml
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-64331-z
銅同位体から推定される火星の分化史 Martian differentiation history inferred from copper isotopes
De-Liang Wang,Dan Zhu,Ying-Kui Xu,Shui-Jiong Wang,Shi-Jie Li,Zi-Ru Liu,Yang Li,Zhi Li,Hong Tang,Xiong-Yao Li & Jian-Zhong Liu
Nature Communications Published:21 October 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-64331-z
Abstract
Sulfide segregation plays an important role in redistributing chalcophile elements during planetary differentiation, yet its efficiency on Mars remains poorly constrained. Here, we report the Cu isotopic evidence for planetary-scale sulfide segregation during martian differentiation. We find that the bulk silicate Mars exhibits a measurable enrichment in isotopically heavy Cu (δ65CuBSMa = −0.03 ± 0.08‰, 2 SD) compared with its chondritic precursors (δ65Cu = −0.30 ± 0.09‰). This isotopic offset cannot be explained by magma ocean devolatilization alone and instead requires preferential incorporation of isotopically light Cu into the core via sulfide segregation. A two-stage core formation model, constrained by established martian building blocks, yields an upper limit for mantle sulfur (400–443 μg/g) with corresponding copper (6–8 μg/g) abundances. These values are consistent with previous estimates for a sulfur-poor martian mantle, as such a mantle facilitates the generation of S-undersaturated melts. Our model further supports a sulfur-rich martian core (~16.1 wt.% S and ~354 μg/g Cu). These findings identify sulfide segregation as a key control on Cu isotopic compositions and chalcophile element budgets during planetary differentiation, providing constraints on Mars’ early evolution.