2025-10-06 大阪大学
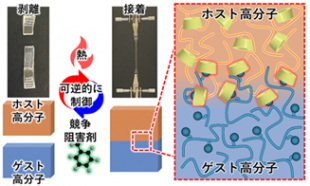
外部刺激による接着・はく離の制御と接着界面におけるナノ構造の可視化
<関連情報>
- https://www.sci.osaka-u.ac.jp/ja/topics/15824/
- https://www.sci.osaka-u.ac.jp/ja/wp-content/uploads/2020/08/【大阪大】PR(中性子で界面構造を解明―はがせるのに強いエコで便利な賢い接着剤―).pdf
- https://advanced.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.202507939
相互拡散を利用した再利用可能かつ解体可能なポリマー接着のための超分子界面工学 Supramolecular Interface Engineering via Interdiffusion for Reusable and Dismantlable Polymer Adhesion
Kenji Yamaoka, Takuma Wada, Iori Ogasa, Takeru Komyo, Chao Luo, Ryohei Ikura, Masahiro Hino, Masako Yamada, Hideki Seto, Yoshihisa Fujii
Advances Materials Published: 03 October 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202507939
Abstract
Controllable adhesion that enables both reuse and dismantling is a key requirement for sustainable materials and device integration. Here,a polymeric adhesion system is demonstrated based on reversible interactions at the interface, in which the association and dissociation of supramolecular complexes are externally regulated by thermal and chemical stimuli. By tuning the glass transition temperature (Tg) of the polymers, chain mobility and complex reformation are simultaneously optimized, leading to enhanced interdiffusion and bond recombination at the adhesion interface. Neutron reflectivity (NR) measurements with deuterium labeling revealed that the interfacial width increased with annealing temperature, reaching up to 24.4 nm at 200 °C after 24 hours. The presence of reversible bonds suppressed polymer interdiffusion despite promoting adhesion strength. The resulting materials exhibit excellent reusability and dismantlability under mild stimuli, with strong potential for applications in recyclable electronics, automotive manufacturing, and temporary assembly technologies.