2025-09-19 東京科学大学
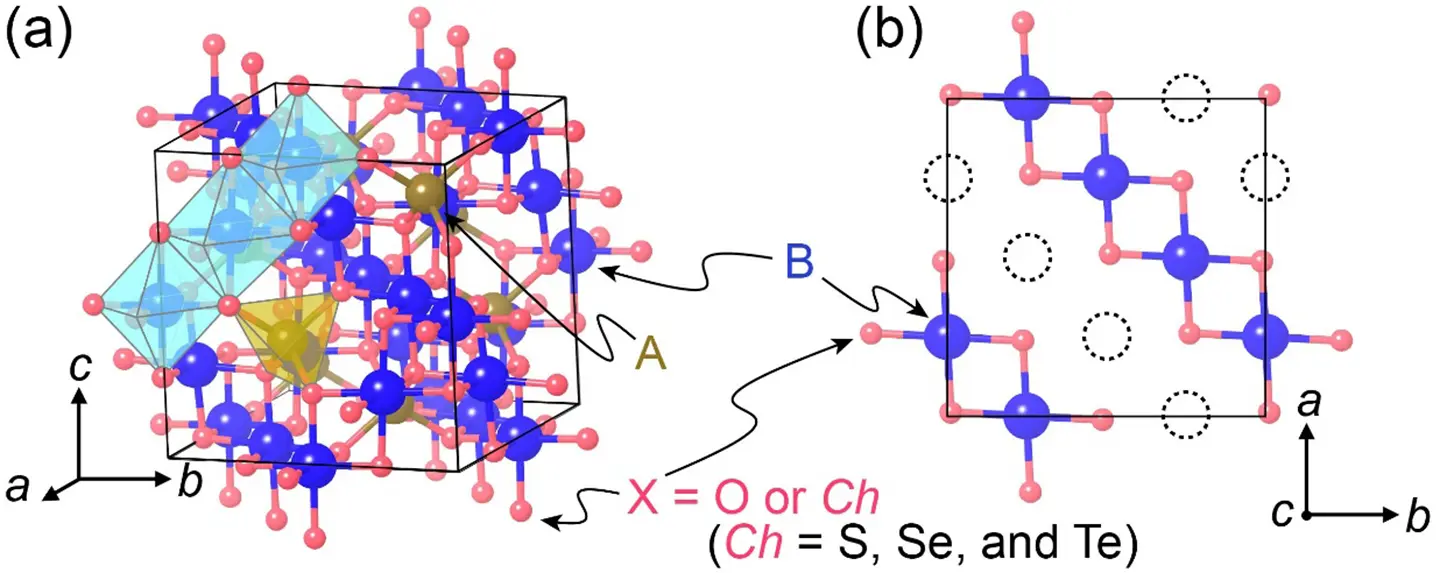
図1. スピネル型構造を有する化合物AB2X4の結晶構造。立方晶の構造でa,b,c軸の格子定数がすべて等しく互いに垂直の関係にあるため高い対称性を有する。(a) 結晶構造の全体像、(b)BとXで構成されるab面。
<関連情報>
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/ja/news/seclrko1m6ag
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/plugins/cms/component_download_file.php?type=2&pageId=&contentsId=1&contentsDataId=2303&prevId=&key=4989c02cb9a422f58c65b2a152788635.pdf
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jacs.5c12816
色調調整可能な直接バンドギャップと両極性ドーパビリティを有するd0陽イオン系スピネル型硫化物半導体d0 Cation-Based Spinel-Type Sulfide Semiconductors with Color-Tunable Direct-Gap and Ambipolar Dopability
Kota Hanzawa,Takayuki Nagai,Ryoga Nagasawa,Takayoshi Katase,Hideo Hosono,and Hidenori Hiramatsu
Journal of the American Chemical Society Published: September 17, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5c12816
Abstract
This work proposes a materials design concept based on chemical bonding and atomic orbital symmetry to realize a direct bandgap and both n- and p-type dopability in spinel-type AB2X4, which have been overlooked as optoelectronic semiconductors. By combining a heavy s0 cation, a d0 cation, and sulfur at the A, B, and X sites, the conduction band minimum is formed mainly by the deep s0 orbital, whereas the valence band maximum is formed by the shallow nonbonding sulfur p orbitals. These are appropriately aligned for n- and p-type doping. Furthermore, the anisotropic d0 orbitals of B suppress dispersion of competing bands, resulting in a direct bandgap. In the candidate ZnSc2S4, the band gap and photoluminescence are widely tuned via isovalent substitution. Additionally, the n- and p-type conductivities can be controlled through chemical doping by over 9 orders of magnitude from the insulating state, validating the effectiveness of our concept in exploring next-generation semiconductors suitable for photoabsorbers of solar cells and green light-emitting diode sources.



