2024-03-25 スイス連邦工科大学ローザンヌ校(EPFL)
<関連情報>
- https://actu.epfl.ch/news/artificial-nanofluidic-synapses-can-store-comput-2/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41928-024-01137-9
メカノイオン・メモリスティック・スイッチを用いたナノ流体ロジック Nanofluidic logic with mechano–ionic memristive switches
Theo Emmerich,Yunfei Teng,Nathan Ronceray,Edoardo Lopriore,Riccardo Chiesa,Andrey Chernev,Vasily Artemov,Massimiliano Di Ventra,Andras Kis &Aleksandra Radenovic
Nature Electronics Published:19 March 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-024-01137-9
Abstract
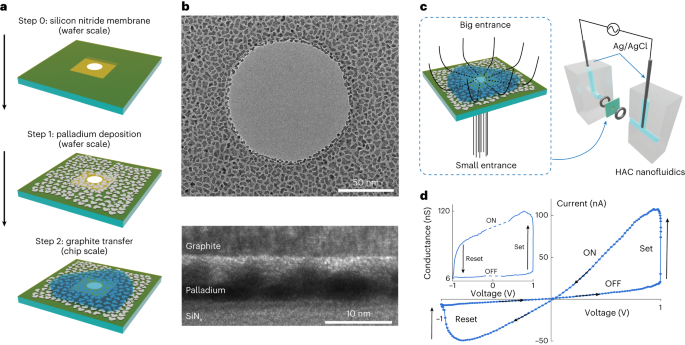
Neuromorphic systems are typically based on nanoscale electronic devices, but nature relies on ions for energy-efficient information processing. Nanofluidic memristive devices could thus potentially be used to construct electrolytic computers that mimic the brain down to its basic principles of operation. Here we report a nanofluidic device that is designed for circuit-scale in-memory processing. The device, which is fabricated using a scalable process, combines single-digit nanometric confinement and large entrance asymmetry and operates on the second timescale with a conductance ratio in the range of 9 to 60. In operando optical microscopy shows that the memory capabilities are due to the reversible formation of liquid blisters that modulate the conductance of the device. We use these mechano–ionic memristive switches to assemble logic circuits composed of two interactive devices and an ohmic resistor.