2024-03-06 米国国立標準技術研究所(NIST)
<関連情報>
- https://www.nist.gov/news-events/news/2024/03/shrinking-technology-expanding-horizons-compact-chips-advance-precision
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07058-z
フォトニックチップを用いた低雑音マイクロ波発振器 Photonic chip-based low-noise microwave oscillator
Igor Kudelin,William Groman,Qing-Xin Ji,Joel Guo,Megan L. Kelleher,Dahyeon Lee,Takuma Nakamura,Charles A. McLemore,Pedram Shirmohammadi,Samin Hanifi,Haotian Cheng,Naijun Jin,Lue Wu,Samuel Halladay,Yizhi Luo,Zhaowei Dai,Warren Jin,Junwu Bai,Yifan Liu,Wei Zhang,Chao Xiang,Lin Chang,Vladimir Iltchenko,Owen Miller,… Scott A. Diddams
Nature Published:06 March 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07058-z
Abstract
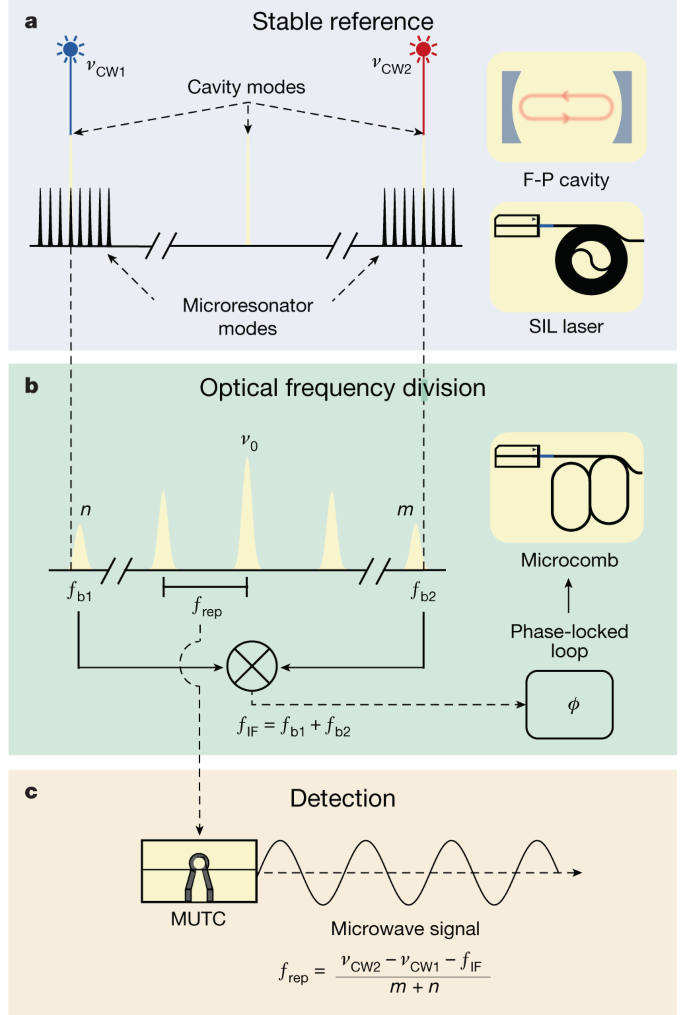
Numerous modern technologies are reliant on the low-phase noise and exquisite timing stability of microwave signals. Substantial progress has been made in the field of microwave photonics, whereby low-noise microwave signals are generated by the down-conversion of ultrastable optical references using a frequency comb1,2,3. Such systems, however, are constructed with bulk or fibre optics and are difficult to further reduce in size and power consumption. In this work we address this challenge by leveraging advances in integrated photonics to demonstrate low-noise microwave generation via two-point optical frequency division4,5. Narrow-linewidth self-injection-locked integrated lasers6,7 are stabilized to a miniature Fabry–Pérot cavity8, and the frequency gap between the lasers is divided with an efficient dark soliton frequency comb9. The stabilized output of the microcomb is photodetected to produce a microwave signal at 20 GHz with phase noise of −96 dBc Hz−1 at 100 Hz offset frequency that decreases to −135 dBc Hz−1 at 10 kHz offset—values that are unprecedented for an integrated photonic system. All photonic components can be heterogeneously integrated on a single chip, providing a significant advance for the application of photonics to high-precision navigation, communication and timing systems.



