2024-03-05 アルゴンヌ国立研究所(ANL)
<関連情報>
- https://www.anl.gov/article/researchers-provide-unprecedented-view-into-aerosol-formation-in-earths-lower-atmosphere
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41561-023-01361-6
対流圏でのエアロゾル形成に関連するCriegee中間体オリゴマー化反応の観測的証拠 Observational evidence for Criegee intermediate oligomerization reactions relevant to aerosol formation in the troposphere
R. L. Caravan,T. J. Bannan,F. A. F. Winiberg,M. A. H. Khan,A. C. Rousso,A. W. Jasper,S. D. Worrall,A. Bacak,P. Artaxo,J. Brito,M. Priestley,J. D. Allan,H. Coe,Y. Ju,D. L. Osborn,N. Hansen,S. J. Klippenstein,D. E. Shallcross,C. A. Taatjes & C. J. Percival
Nature Geoscience Published:05 March 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41561-023-01361-6
Abstract
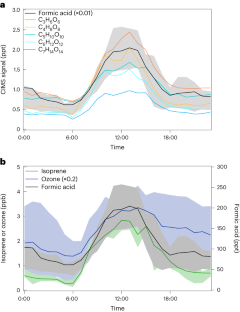
Criegee intermediates are reactive intermediates that are implicated in transforming the composition of Earth’s troposphere and in the formation of secondary organic aerosol, impacting Earth’s radiation balance, air quality and human health. Yet, direct identification of their signatures in the field remains elusive. Here, from particulate and gas-phase mass-spectrometric measurements in the Amazon rainforest, we identify sequences of masses consistent with the expected signatures of oligomerization of the CH2OO Criegee intermediate, a process implicated in ozonolysis-driven aerosol formation. We assess the potential contributions of oligomerization through laboratory ozonolysis experiments, direct kinetic studies of Criegee intermediate reactions, and high-level theoretical calculations. Global atmospheric models built on these kinetics results indicate that Criegee intermediate chemistry may play a larger role in altering the composition of Earth’s troposphere than is captured in current atmospheric models, especially in areas of high humidity. However, the models still capture only a relatively small fraction of the observed signatures, suggesting considerable underestimates of Criegee intermediate concentrations and reactivity and/or the dominance of other, presently uncharacterized, oxidation mechanisms. Resolving the remaining uncertainties in emission inventories and the effects of atmospheric water vapour on key chemical reactions will be required to definitively assess the role of Criegee intermediate oligomerization reactions.



