2024-02-14 アルゴンヌ国立研究所(ANL)
<関連情報>
- https://www.anl.gov/article/argonne-scientists-use-ai-to-identify-new-materials-for-carbon-capture
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s42004-023-01090-2
炭素捕獲用有機金属骨格設計のための分子拡散モデルに基づく生成的人工知能フレームワーク A generative artificial intelligence framework based on a molecular diffusion model for the design of metal-organic frameworks for carbon capture
Hyun Park,Xiaoli Yan,Ruijie Zhu,Eliu A. Huerta,Santanu Chaudhuri,Donny Cooper,Ian Foster & Emad Tajkhorshid
Communications Chemistry Published:14 February 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s42004-023-01090-2
Abstract
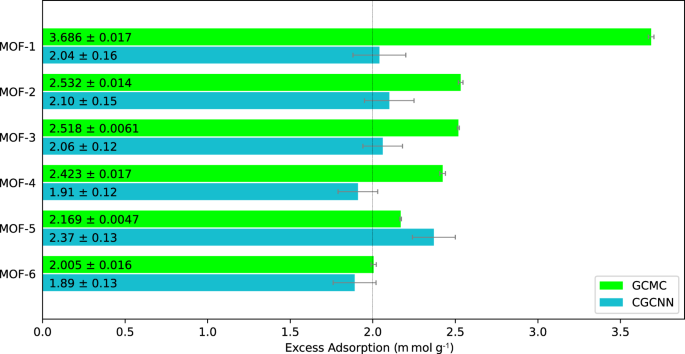
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) exhibit great promise for CO2 capture. However, finding the best performing materials poses computational and experimental grand challenges in view of the vast chemical space of potential building blocks. Here, we introduce GHP-MOFassemble, a generative artificial intelligence (AI), high performance framework for the rational and accelerated design of MOFs with high CO2 adsorption capacity and synthesizable linkers. GHP-MOFassemble generates novel linkers, assembled with one of three pre-selected metal nodes (Cu paddlewheel, Zn paddlewheel, Zn tetramer) into MOFs in a primitive cubic topology. GHP-MOFassemble screens and validates AI-generated MOFs for uniqueness, synthesizability, structural validity, uses molecular dynamics simulations to study their stability and chemical consistency, and crystal graph neural networks and Grand Canonical Monte Carlo simulations to quantify their CO2 adsorption capacities. We present the top six AI-generated MOFs with CO2 capacities greater than 2m mol g−1, i.e., higher than 96.9% of structures in the hypothetical MOF dataset.