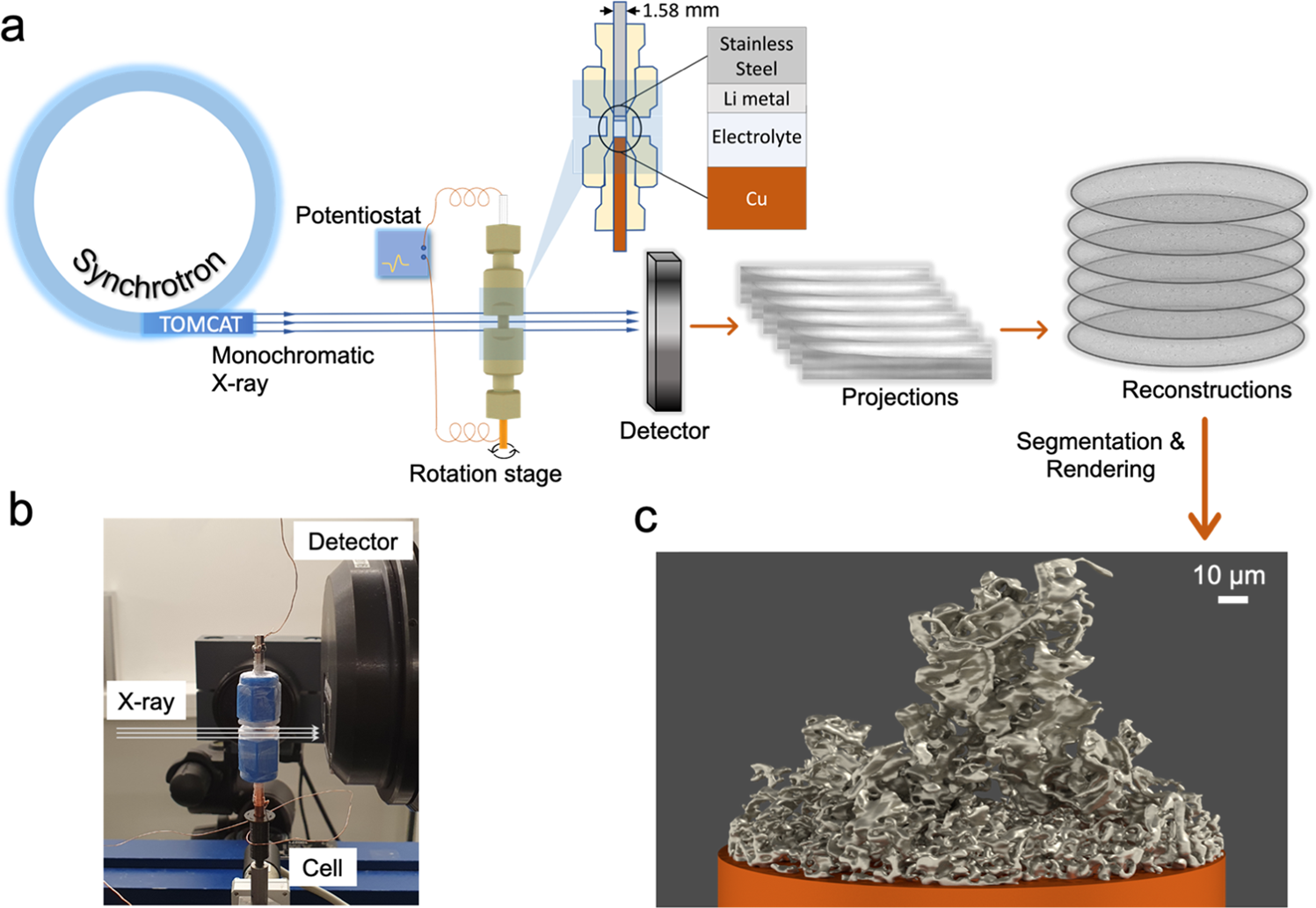
世界の気候目標を達成するには、1つの炭素除去手段だけでは不十分です Meeting the world’s climate goals will take more than one form of carbon removal
2023-03-09 パシフィック・ノースウェスト国立研究所(PNNL)
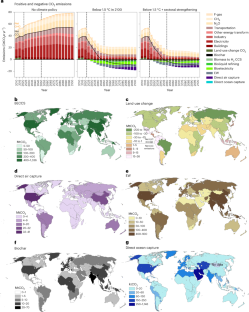
森林再生から風化促進法による炭素固定まで、6つの異なる方法の炭素除去ポテンシャルが示され、これらがうまく組み合わされることで年間100億トンの二酸化炭素除去が必要だという。それぞれの方法には、利点と問題があり、個々の地域に合わせた方針が必要とされる。しかし、課題の一つは、メタンや亜酸化窒素といった、二酸化炭素以外の温室効果ガスも対象とすべきであるということである。
<関連情報>
- https://www.pnnl.gov/news-media/diverse-approach-key-carbon-removal
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41558-023-01604-9
多様な二酸化炭素除去アプローチにより、エネルギー-水-土地システムへの影響を軽減できる可能性がある Diverse carbon dioxide removal approaches could reduce impacts on the energy–water–land system
Jay Fuhrman,Candelaria Bergero,Maridee Weber,Seth Monteith,Frances M. Wang,Andres F. Clarens,Scott C. Doney,William Shobe & Haewon McJeon
Nature Climate Change Published:09 March 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-023-01604-9
Abstract
Carbon dioxide removal (CDR) is a critical tool in all plans to limit warming to below 1.5 °C, but only a few CDR pathways have been incorporated into integrated assessment models that international climate policy deliberations rely on. A more diverse set of CDR approaches could have important benefits and costs for energy–water–land systems. Here we use an integrated assessment model to assess a complete suite of CDR approaches including bioenergy with carbon capture and storage, afforestation, direct air capture with carbon storage, enhanced weathering, biochar and direct ocean capture with carbon storage. CDR provided by each approach spans three orders of magnitude, with deployment and associated impacts varying between regions. Total removals reach approximately 10 GtCO2 yr−1 globally, largely to offset residual CO2 and non-CO2 emissions, which remain costly to avoid even under scenarios specifically designed to reduce them.