2026-02-11 ミュンヘン大学(LMU)
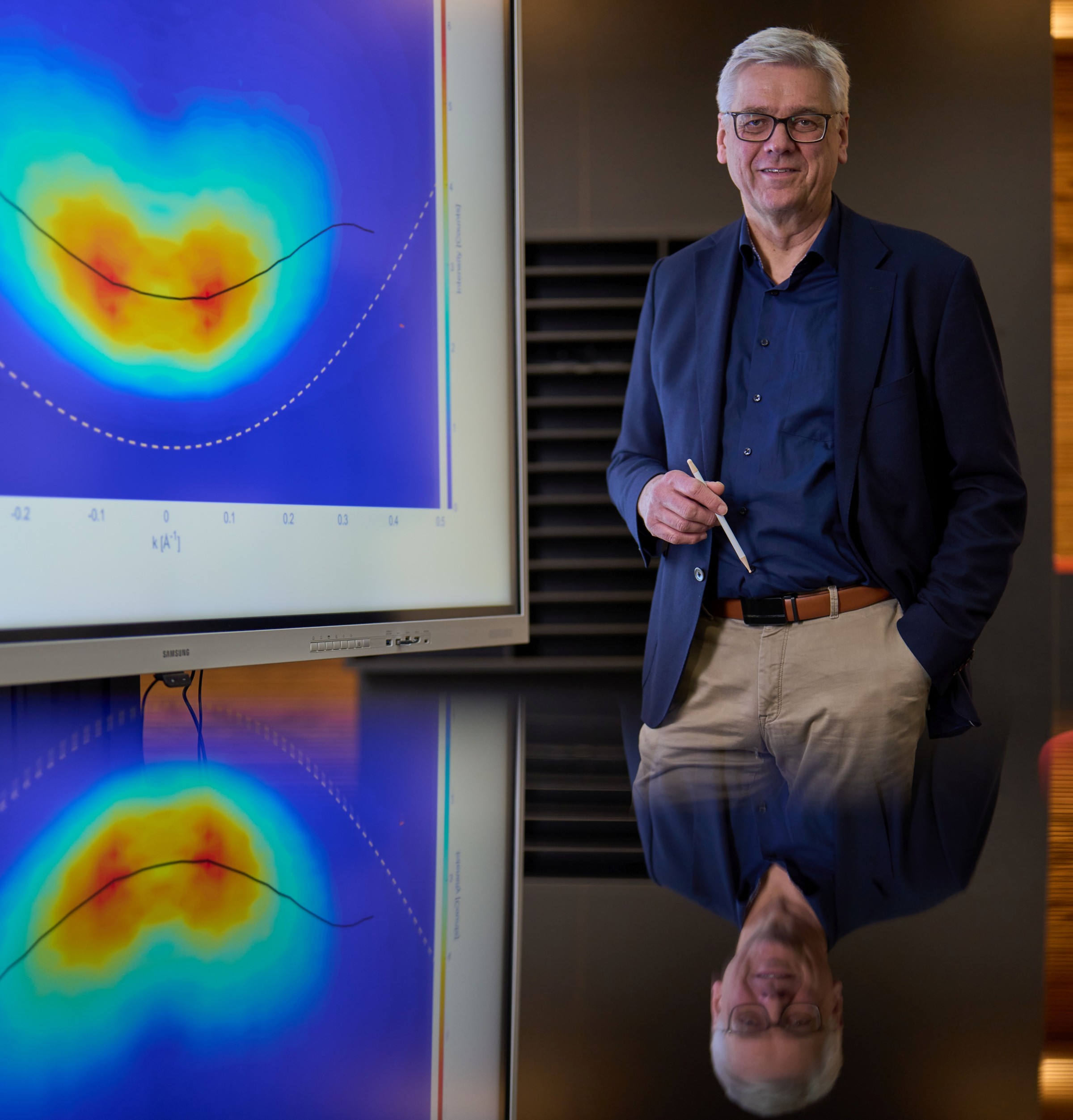
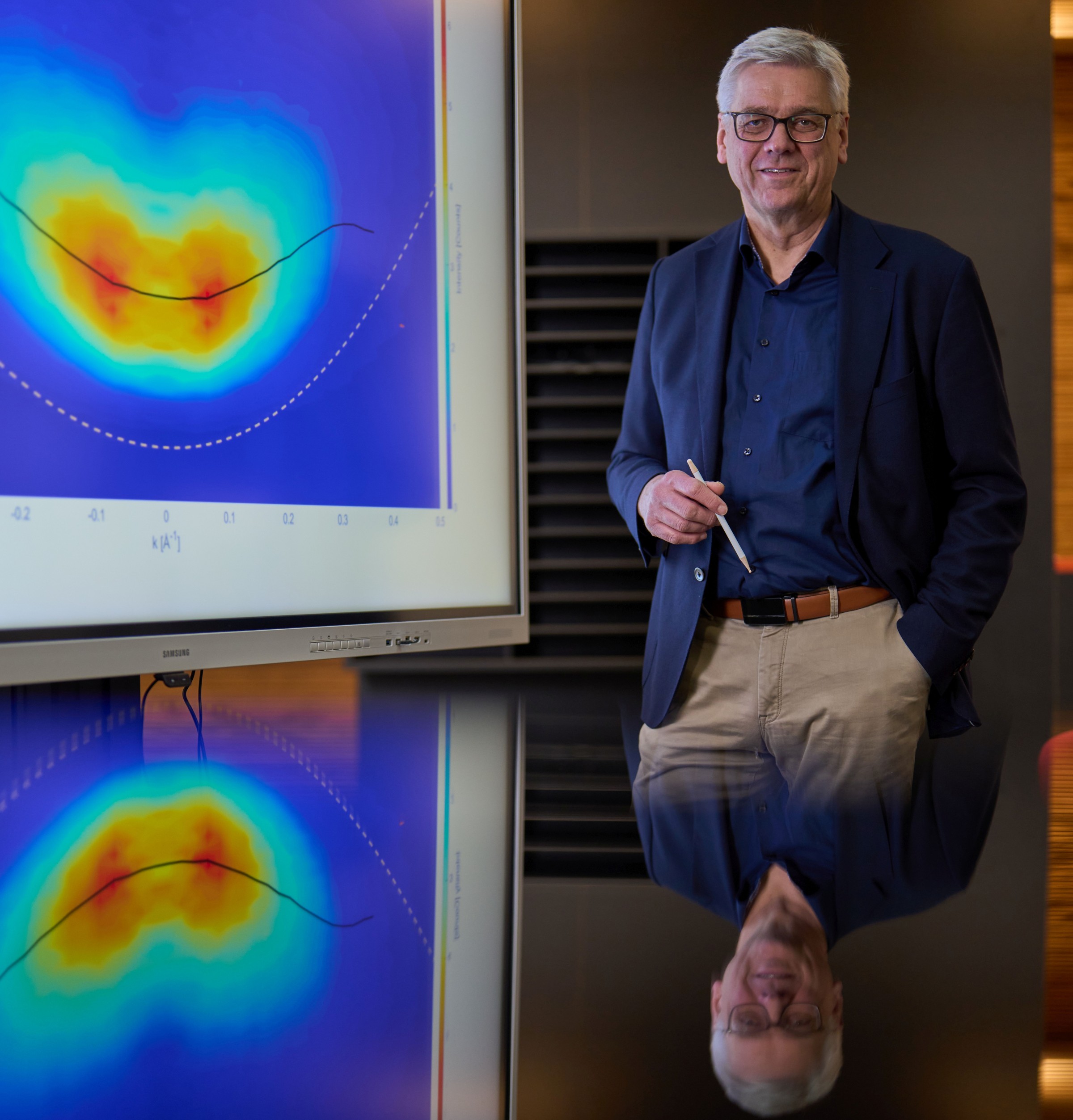
Their study is “of great value for the scientific community and will help both in the planning of further experiments and in the development of various devices.”, says LMU-physicist Jochen Feldmann. The measured distribution of electrons at time zero can be seen on the screen. © Jan Greune / LMU
<関連情報>
- https://www.lmu.de/en/newsroom/news-overview/news/semiconductor-physics-polaron-formation-observed-for-first-time-6f8cc5f3.html
- https://journals.aps.org/prmaterials/abstract/10.1103/wcq2-gpmz
BiOIナノプレートレットにおけるフレーリッヒポーラロン形成の直接観察 Direct observation of Fröhlich polaron formation in BiOI nanoplatelets
Matthias F. Kestler, Kyung Chul Woo, Justin W. X. Lim, Lucas M. Prins, Jochen Feldmann, and Zhi-Heng Loh
Physical Review Materials Published: 11 February, 2026
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1103/wcq2-gpmz
Abstract
For large polarons, Fröhlich theoretically derived an increased effective mass and a decreased energy as compared to free charge carriers. These changes have hitherto eluded direct observation. Here, we report on the direct observation of large polaron formation after photoexcitation in BiOI nanoplatelets, a system known to host spatially separated e-h pairs. We employ time- and momentum-resolved photoemission electron microscopy with 50-fs pulses to monitor the dynamics of the conduction-band (CB) dispersion (). Indeed, we observe a doubling of the effective mass accompanied by a decrease of the CB energy leading to an overall drop of 160 meV.