2026-01-26 中国科学院(CAS)
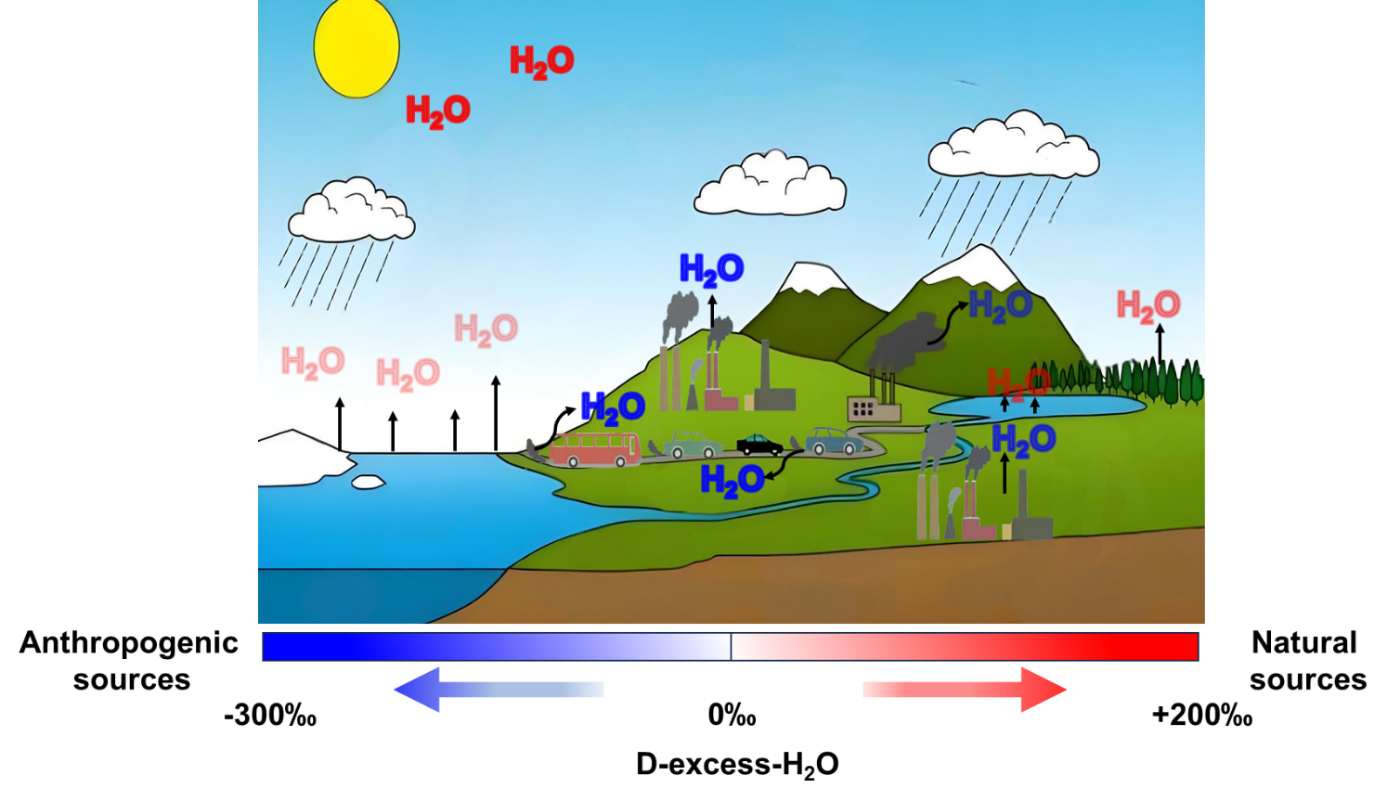
Schematic diagram showing the composition of water vapor d-excessv from anthropogenic sources and natural sources. (Image by IEE)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research-news/202602/t20260210_1150383.shtml
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.est.5c08595
異なる化石燃料からの燃焼由来水蒸気同位体組成の測定 Measurements of Combustion-Derived Water Vapor Isotopic Composition from Different Fossil Fuels
Meng Xing,Junji Cao,Zhoufeng Wang,Qiyuan Wang,Wenwu Cai,Jie Tian,Jianjun Li,and Weiguo Liu
Environmental Science & Technology Published: January 14, 2026
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5c08595
Abstract
Fossil fuel combustion not only emits large amounts of CO2 but also generates significant water vapor (H2Ov). Currently, research on the isotopic composition of combustion-derived water vapor (CDWV) predominantly relies on theoretical calculations. This has hindered the comprehensive understanding of the characteristic patterns in isotopic variations and associated isotopic fractionation mechanisms during CDWV formation. In this study, we systematically investigated the variation characteristics in the isotopic composition of water vapor emitted from the combustion of various fuels and initially established the characteristic isotopic signatures of CDWV. The δ18O–H2Ov produced by fossil fuel combustion inherits the isotopic signature of atmospheric O2, resulting in a significantly positive δ18Ov value (> +10‰) and markedly negative d-excessv (< −200‰) characteristic. Through this study, we demonstrated the reliability and universality of the theoretical values of CDWV isotopic composition. Through experiments, we observed the dynamic variations in isotopic compositions and water vapor mixing ratios during fossil fuel combustion processes. The distinct isotopic disparity between the CDWV and the natural water vapor enables us to use d-excessv as a quantitative tracer for estimating the contribution of anthropogenic fossil fuel combustion to atmospheric moisture.



