2026-01-16 カーディフ大学
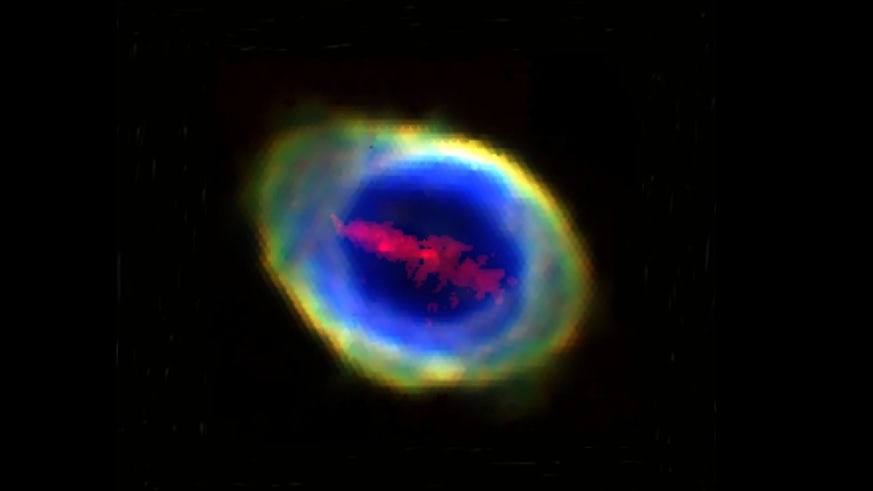
A composite RGB image of the Ring Nebula (also known as Messier 57 and NGC 6720) constructed from four WEAVE/LIFU line maps. The bright outer ring is made up of emission from three different ions of oxygen, while the ‘bar’ across the middle is due to a plasma of four-times ionised iron atoms. Credit: R. Wesson, Cardiff University/UCL.
<関連情報>
- https://www.cardiff.ac.uk/news/view/3005580-mysterious-iron-bar-discovered-in-famous-nebula
- https://academic.oup.com/mnras/article/546/1/staf2139/8425243
NGC 6720のWEAVEイメージング分光:リング内の鉄の棒 WEAVE imaging spectroscopy of NGC 6720: an iron bar in the Ring
R Wesson,J E Drew,M J Barlow,J García-Rojas,R Greimel,D Jones,A Manchado,R A H Morris,A Zijlstra,P J Storey,…
Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society Published:16 January 2026
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1093/mnras/staf2139
ABSTRACT
We present spatially resolved spectroscopic observations of the planetary nebula NGC 6720, the Ring Nebula, taken during the science verification phase of WEAVE, a new instrument mounted on the William Herschel Telescope on La Palma. We use the instrument’s Large Integral Field Unit (LIFU) to obtain spectra of the Ring Nebula, covering its entire optically bright inner regions as well as parts of its much fainter outer molecular halo. We report the discovery of emission from [Fe v] and [Fe vi] confined to a narrow ‘bar’ extending across the central regions of the nebula. No lines of other elements share this morphology or, at the spectral resolving power used (|$R \sim 2500$|R~2500), the same radial velocity. The extent to which iron in this bar is depleted is presently unclear; comparison with JWST-detected dust continuum emission suggests that some dust grain destruction may be occurring in the region, but there is currently no observational evidence for the>-1T>106



