2025-12-18 中国科学院(CAS)
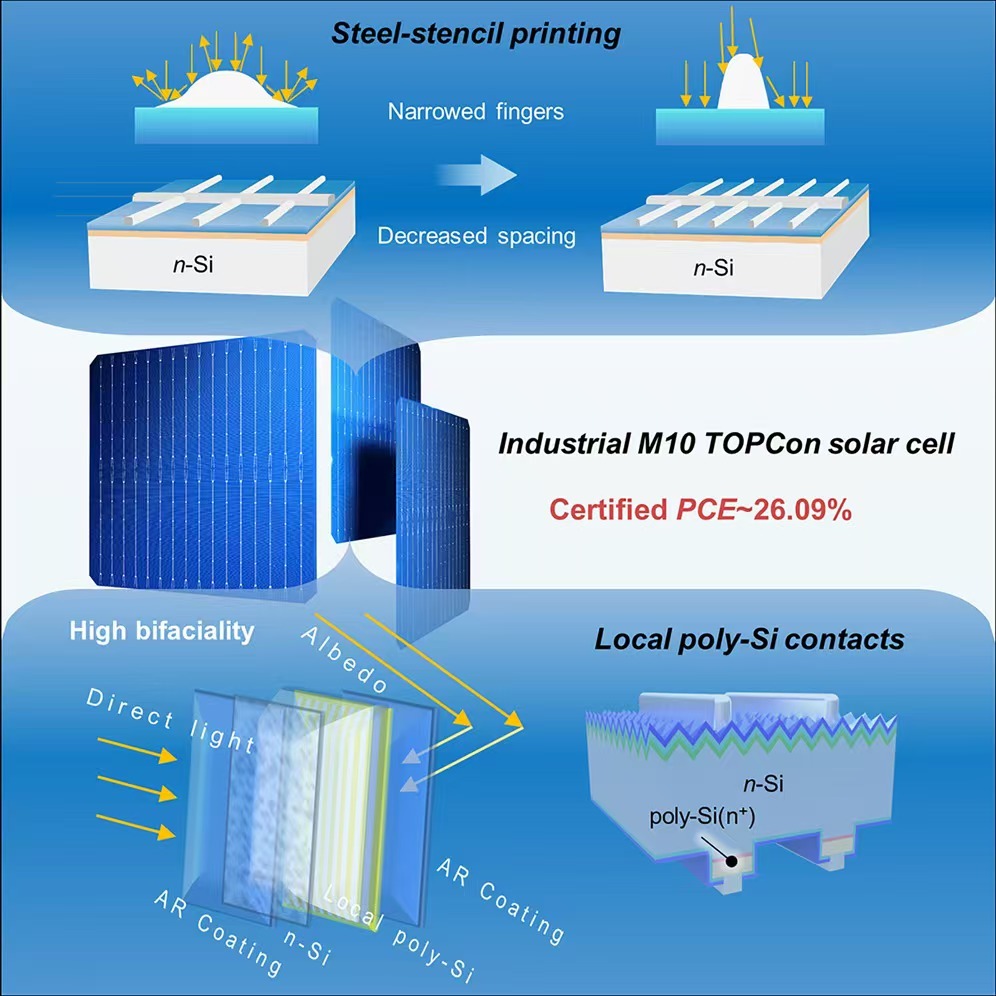
The high-efficiency industrial TOPCon solar cells. (Image by NIMTE)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/tech/202512/t20251219_1137997.shtml
- https://www.cell.com/joule/abstract/S2542-4351(25)00412-X
スチールステンシル印刷と局所ポリシリコンコンタクトにより、効率26.09%の産業グレードのトンネル酸化物パッシベーションコンタクト太陽電池を実現 Steel-stencil printing and local polysilicon contacts enable 26.09%-efficient industrial-grade tunnel oxide passivating contact solar cells
Haojiang Du ∙ Weiming Lu ∙ Xinrui An ∙ … ∙ Zhenhai Yang ∙ Yuheng Zeng, ∙ Jichun Ye
Joule Published:December 12, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joule.2025.102231
Context & scale
Crystalline silicon photovoltaics constitute the cornerstone of the global transition to renewable energy, with tunnel oxide passivating contact (TOPCon) technology emerging as the dominant industrial solution due to its exceptional efficiency potential and favorable cost-effectiveness. Nevertheless, a significant challenge persists in balancing efficiency, manufacturing cost, and bifacial energy yield. Overcoming this efficiency-cost-bifaciality trilemma is crucial for enhancing the competitiveness and accelerating the deployment of TOPCon technology. This work presents a mass-production-ready strategy that integrates a high-precision front-side steel-stencil printing process, which reduces silver consumption and improves current collection, with a rear-side local polysilicon contact design that minimizes parasitic absorption. This co-optimization enables a certified 26.09% efficiency on industry-standard M10 wafers, coupled with high bifaciality. By demonstrating a viable path to simultaneously enhance efficiency, lower silver consumption, and unlock bifacial gains, this work provides a scalable blueprint for photovoltaic manufacturing, strengthening the position of TOPCon technology for terawatt-scale sustainable energy deployment.
Highlights
- Steel-stencil printing enables narrow fingers and reduced silver consumption
- Optimized silver paste improves the silver-silicon contact properties
- Local polysilicon design minimizes parasitic absorption for high bifaciality
- A certified efficiency of 26.09% is achieved on an industrial M10 wafer
Summary
Tunnel oxide passivating contact (TOPCon) solar cells (SCs) have emerged as the dominant crystalline silicon technology in the photovoltaic industry. However, further improving efficiency while simultaneously reducing silver consumption for TOPCon SCs remains a significant challenge. Here, we propose a synergistic strategy integrating high-precision steel-stencil printing technology and a local polysilicon contact design, achieving a certified efficiency of 26.09% on industrial-grade M10 silicon wafers. Specifically, transitioning from conventional screen printing to steel-stencil printing enables the fabrication of ultra-narrow fingers and a substantial reduction in silver consumption. The optimized silver paste formulation facilitates the formation of densely packed silver nanoparticles at the silver/silicon interface, resulting in lower contact resistivity. Additionally, our laser-patterned local polysilicon contact design effectively optimizes the trade-off between carrier transport and parasitic absorption losses while achieving high bifaciality (∼90%) that is beneficial for practical energy yield.