2025-11-24 ワシントン州立大学 (WSU)
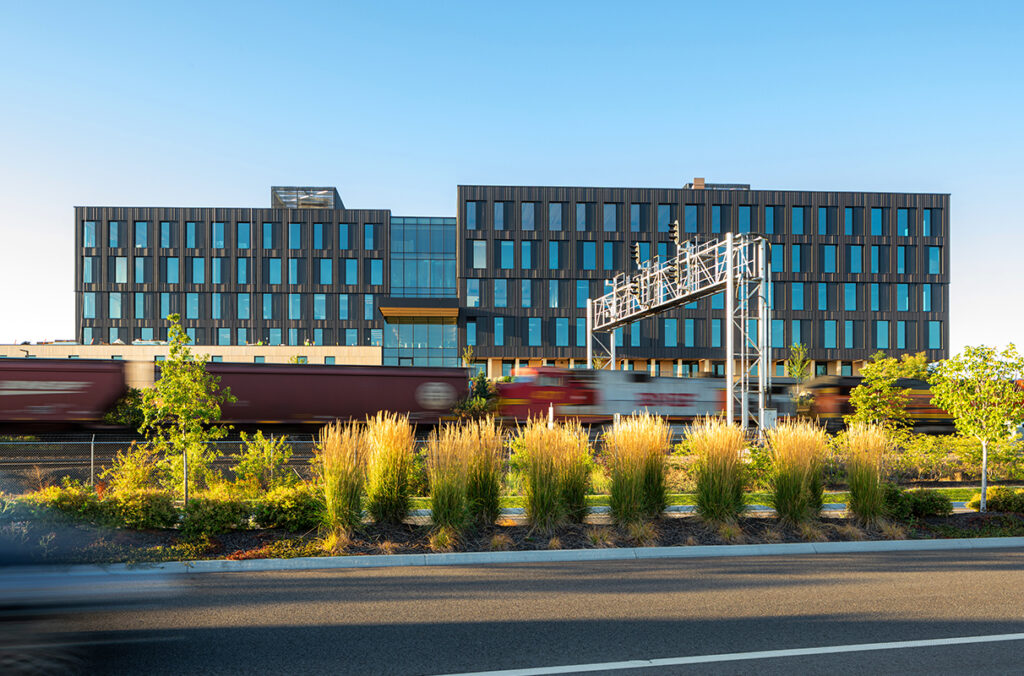

For the work, the researchers used battery assets and electricity feeders in Spokane’s Catalyst Building and South Landing Eco-District (photo courtesy of WSU Spokane).
<関連情報>
- https://news.wsu.edu/news/2025/11/24/researchers-test-electricity-trading-system-that-could-cut-costs-for-residents/
- https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/11034748
グリッドエッジシステムを実現するためのコミュニティベースのトランザクティブコーディネーションメカニズム Community-Based Transactive Coordination Mechanism for Enabling Grid-Edge Systems
John R. Theisen; Anjan Bose; Monish Mukherjee; Dan Burgess; Kenneth Wilhelm; Zoë Oens,…
IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications Published:13 June 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2025.3579436
Abstract
The changing landscape of the electricity industry, characterized by a surge in distributed energy resources (DERs) and proactive customers, necessitates practical solutions for coordinated operation especially at the distribution-level. This paper introduces a community-based transactive coordination mechanism designed to incentivize customers for providing localized and system-level services reflected through real-time prices. The work presents a bidding approach for communities, representing collectives of customers, to formulate their price-responsiveness for retail energy coordination, emphasizing a community-centric model. By sending bidding curves to a third-party, the mechanism enables customers with DER assets to actively participate in localized coordination with the Load Serving Entity (LSE), supplementing each other’s and even the utility’s needs through a shared energy economy. The proposed transactive mechanism is implemented leveraging a co-simulation framework that integrates a distribution grid simulator with control agents for performance evaluation. Simulation-based evaluation on a real distribution system use-case, in collaboration with a local utility, demonstrate the potential of the mechanism to reduce energy costs up to 12% for communities with DERs like solar photovoltaic (PV) and battery energy storage systems (BESS). The mechanism’s effectiveness is further validated through field tests conducted on a utility’s real system, utilizing a 1.32 MWh battery resource.