2025-09-18 東京科学大学
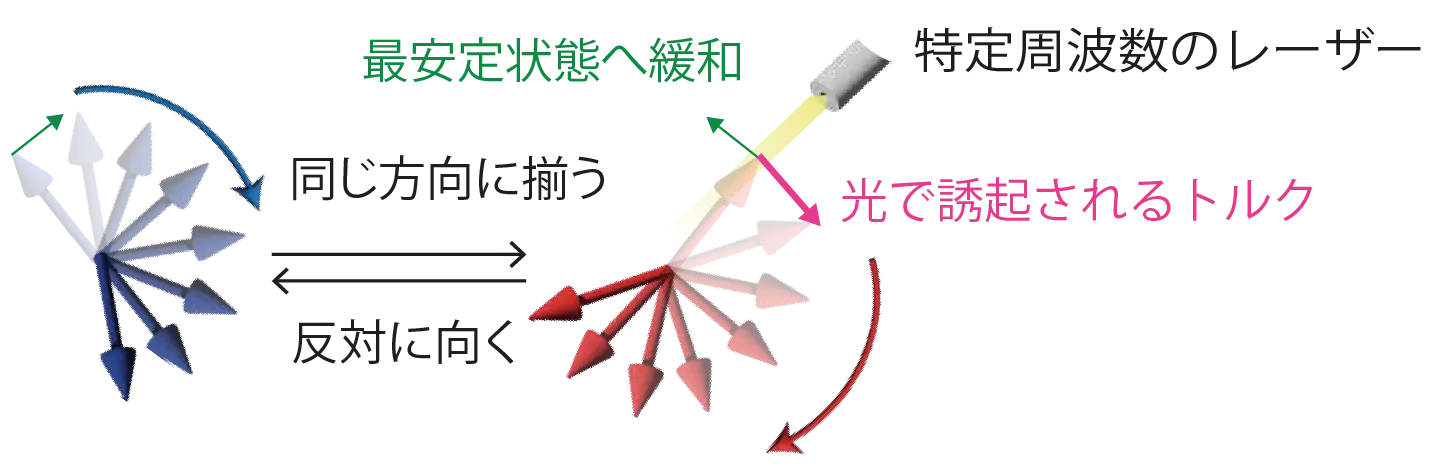
図1. 本研究で提案した磁化の間の非相反相互作用。作用反作用の法則を実効的に破っている
<関連情報>
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/ja/news/omkj3iusezd1
- https://www.isct.ac.jp/plugins/cms/component_download_file.php?type=2&pageId=&contentsId=1&contentsDataId=2261&prevId=&key=9dbe659bdb66db73e59046cba22aa5f8.pdf
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-62707-9
光誘起非互換磁性 Photoinduced non-reciprocal magnetism
Ryo Hanai,Daiki Ootsuki & Rina Tazai
Nature Communications Published:18 September 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-62707-9
Abstract
Out of equilibrium, the action-reaction symmetry of interactions is often broken, leading to the emergence of various collective phenomena with no equilibrium counterparts. Although ubiquitous in classical active systems, implementing such non-reciprocal interactions in solid-state systems has remained challenging, as known quantum schemes require precise single-site control. Here, we propose a dissipation-engineering protocol that induces non-reciprocal interactions in solid-state platforms with light, which we expect to be achievable with state-of-the-art experimental techniques. Focusing on magnetic metals, we show microscopically that a light injection that introduces a decay channel to a virtually excited state gives rise to non-reciprocal interactions between localized spins, resulting in chase-and-runaway dynamics. Applying our scheme to layered ferromagnets, we show that a non-reciprocal phase transition to a many-body time-dependent chiral phase occurs. Our work paves the way to bring solid-state systems to the realm of non-reciprocal science, providing yet another possibility to control quantum matter with light.