2025-09-18 中国科学院(CAS)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/cas_media/202509/t20250918_1055010.shtml
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-09561-3
常温充電可能な全固体水素化物イオン電池 A room temperature rechargeable all-solid-state hydride ion battery
Jirong Cui,Ren Zou,Weijin Zhang,Hong Wen,Jinyao Liu,Shangshang Wang,Shukun Liu,Hetong Chen,Wei Liu,Xiaohua Ju,Weiwei Wang,Tao Gan,Jiong Li,Jianping Guo,Teng He,Hujun Cao & Ping Chen
Nature Published:17 September 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-025-09561-3
Abstract
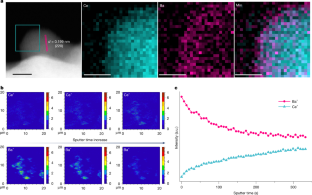
As a negative charge carrier, the hydride ion (H−) is more energetic, polarizable and reactive than cations1. An H−-mediated electrochemical process is fundamentally different from existing systems and enables the development of innovative electrochemical devices, such as rechargeable batteries, fuel cells, electrolysis cells and gas separation membranes2. Here we developed a core-shell hydride 3CeH3@BaH2, which exhibits fast H− conduction at ambient temperature and becomes a superionic conductor above 60 °C. This hydride allows us to construct an all-solid-state rechargeable H− battery CeH2|3CeH3@BaH2|NaAlH4, which operates at ambient conditions using NaAlH4 and CeH2 as cathode and anode materials, respectively. This battery has an initial specific capacity of 984 mAh g−1 and retains 402 mAh g−1 after 20 cycles. Using hydrogen as charge carriers can avoid the formation of detrimental metal dendrites, in principle, which creates new research avenues for clean energy storage and conversion.



