2025-09-15 ピッツバーグ大学
<関連情報>
データは自ら語る:品質主導型ワイヤレス合成データの活用 Data Can Speak for Itself: Quality-guided Utilization of Wireless Synthetic Data
Chen Gong, Bo Liang, Wei Gao, Chenren Xu
arXiv Submitted on 29 Jun 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2506.23174
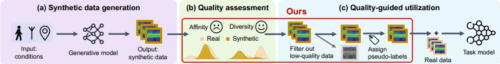
Abstract
Generative models have gained significant attention for their ability to produce realistic synthetic data that supplements the quantity of real-world datasets. While recent studies show performance improvements in wireless sensing tasks by incorporating all synthetic data into training sets, the quality of synthetic data remains unpredictable and the resulting performance gains are not guaranteed. To address this gap, we propose tractable and generalizable metrics to quantify quality attributes of synthetic data – affinity and diversity. Our assessment reveals prevalent affinity limitation in current wireless synthetic data, leading to mislabeled data and degraded task performance. We attribute the quality limitation to generative models’ lack of awareness of untrained conditions and domain-specific processing. To mitigate these issues, we introduce SynCheck, a quality-guided synthetic data utilization scheme that refines synthetic data quality during task model training. Our evaluation demonstrates that SynCheck consistently outperforms quality-oblivious utilization of synthetic data, and achieves 4.3% performance improvement even when the previous utilization degrades performance by 13.4%.



