2025-07-29 中国科学院(CAS)
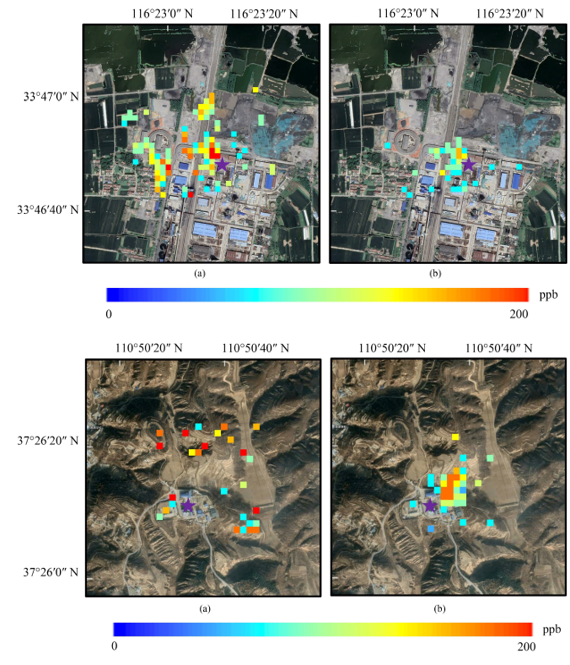
Comparison of detection performance before and after signal interference suppression under different surface background conditions. (Image by WU Shichao)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/phys/202507/t20250729_1048659.shtml
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1569843225003115?via%3Dihub
kMetha-Mamba: メタンプルームセグメンテーションのためのK平均法クラスタリングMamba kMetha-Mamba: K-means clustering mamba for methane plumes segmentation
Yuquan Liu, Hailiang Shi, Ke Cao, Shichao Wu, Hanhan Ye, Xianhua Wang, Erchang Sun, Yunfei Han, Wei Xiong
International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation Available online: 25 June 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2025.104664
Highlights
- Introduces kMetha-Mamba: a novel methane plumes segmentation network.
- Custom-designed Mamba block for updating cluster centers.
- Achieves excellent performance across multiple datasets.
Abstract
Monitoring and curbing methane emissions is an important means of slowing global warming. Existing quantitative segmentation methods based on convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and Transformers are limited in their ability to process large-scale remote sensing images. They are also susceptible to interference from species with similar spectral features, resulting in high false positive rates. To cope with these difficulties, we propose kMetha-Mamba — a k-means clustering mamba-based network for methane plumes segmentation. Specifically, the spatial feature encoder (SFE) is employed to extract clustering patches from the methane enhancement product for follow-up complementary learning with spectral information. Subsequently, similar pixels are clustered based on the ability of spectral derivative to distinguish between subtle spectral variations in a continuous region and species with similar spectral features. However, traditional k-means clustering algorithms are susceptible to the influence of outliers. In this study, we revisit the relationship between pixels and the selective scanning mechanism from the perspective of clustering, and propose k-means mamba to implement cluster center updating by multi-directional local scanning, which mitigates the effect of outliers on cluster centers. Finally, kMetha-Mamba utilizes a mamba-based decoder (MBD) with linear complexity and long-range dependencies to achieve high efficiency and precision segmentation. Extensive experiments on hyperspectral and multispectral datasets from different sensors have shown that kMetha-Mamba has the best performance compared to the state-of-the-art methods. Among them, it achieve the highest accuracy of 88.69% and the lowest false positive rates of 0.0466% on the AVIRIS-NG dataset.