2025-06-24 京都大学
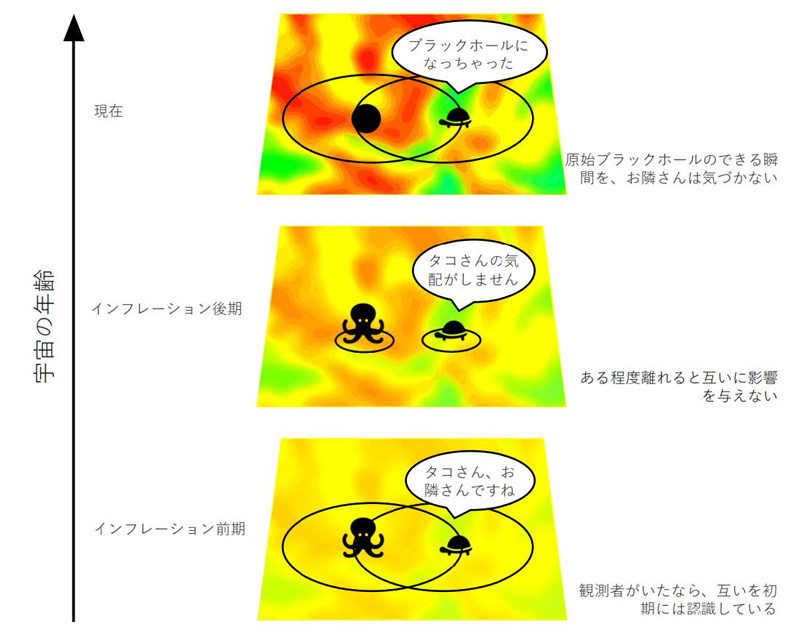
インフレーション中に、量子ゆらぎが増幅される様子を模式的に表している。赤い領域は高密度領域、黄色い領域は低密度を表す。極端な高密度領域はブラックホールに崩壊し、原始ブラックホールを形成する可能性がある。
<関連情報>
- https://www.kyoto-u.ac.jp/ja/research-news/2025-06-24-2
- https://www.kyoto-u.ac.jp/sites/default/files/2025-06/web_2506_Artigas-42b542217a61936cb819388441f96311.pdf
- https://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.134.221001
拡張された形式論: 非空間的に平坦な分離宇宙アプローチ Extended Formalism: Nonspatially Flat Separate-Universe Approach
Danilo Artigas, Shi Pi, and Takahiro Tanaka
Physical Review Letters Published: 3 June, 2025
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.134.221001
Abstract
The formalism is a powerful approach to compute nonlinearly the large-scale evolution of the comoving curvature perturbation . It assumes a set of FLRW patches that evolve independently, but in doing so, all the gradient terms are discarded, which are not negligibly small in models beyond slow roll. In this Letter, we extend the formalism to capture these gradient corrections by encoding them in a homogeneous-spatial-curvature contribution assigned to each FLRW patch. For a concrete example, we apply this formalism to the ultra-slow-roll inflation, and find that it can correctly describe the large-scale evolution of the comoving curvature perturbation from the horizon exit. We also briefly discuss non-Gaussianities in this context.