2025-06-11 ジョンズ・ホプキンス大学
<関連情報>
- https://hub.jhu.edu/2025/06/11/telescopes-look-at-cosmic-dawn/
- https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/1538-4357/adc723
CLASSによる最大スケールのCMB Eモード偏光の測定 A Measurement of the Largest-scale CMB E-mode Polarization with CLASS
Yunyang Li (李云炀), Joseph R. Eimer, John W. Appel, Charles L. Bennett, Michael K. Brewer, Sarah Marie Bruno, Ricardo Bustos, Carol Yan Yan Chan, David T. Chuss, Joseph Cleary,…
The Astrophysical Journal Published: 2025 June 11
DOI:10.3847/1538-4357/adc723
Abstract
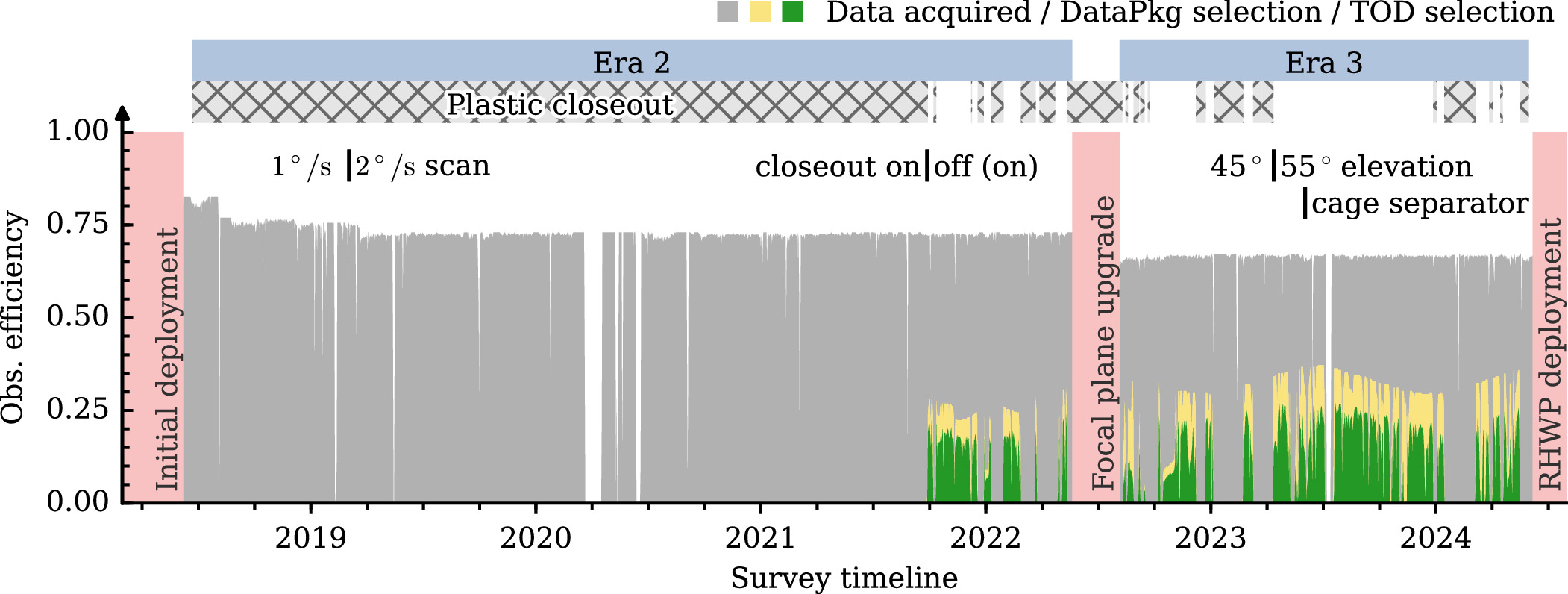
We present measurements of large-scale cosmic microwave background E-mode polarization from the Cosmology Large Angular Scale Surveyor 90 GHz data. Using 115 det-yr of observations collected through 2024 with a variable-delay polarization modulator, we achieved a polarization sensitivity of 82μKarcmin, comparable to Planck at similar frequencies (100 and 143 GHz ). The analysis demonstrates effective mitigation of systematic errors and addresses challenges to large-angular-scale power recovery posed by time-domain filtering in maximum-likelihood map-making. A novel implementation of the pixel-space transfer matrix is introduced, which enables efficient filtering simulations and bias correction in the power spectrum using the quadratic cross-spectrum estimator. Overall, we achieved an unbiased time-domain filtering correction to recover the largest angular scale polarization, with the only power deficit, arising from map-making nonlinearity, being characterized as <3%. Through cross-correlation with Planck, we detected the cosmic reionization at 99.4% significance and measured the reionization optical depth τ=0.053+0.018−0.019, marking the first ground-based attempt at such a measurement. At intermediate angular scales (ℓ > 30), our results, both independently and in cross-correlation with Planck, remain fully consistent with Planck’s measurements.