2025-05-30 中国科学院(CAS)
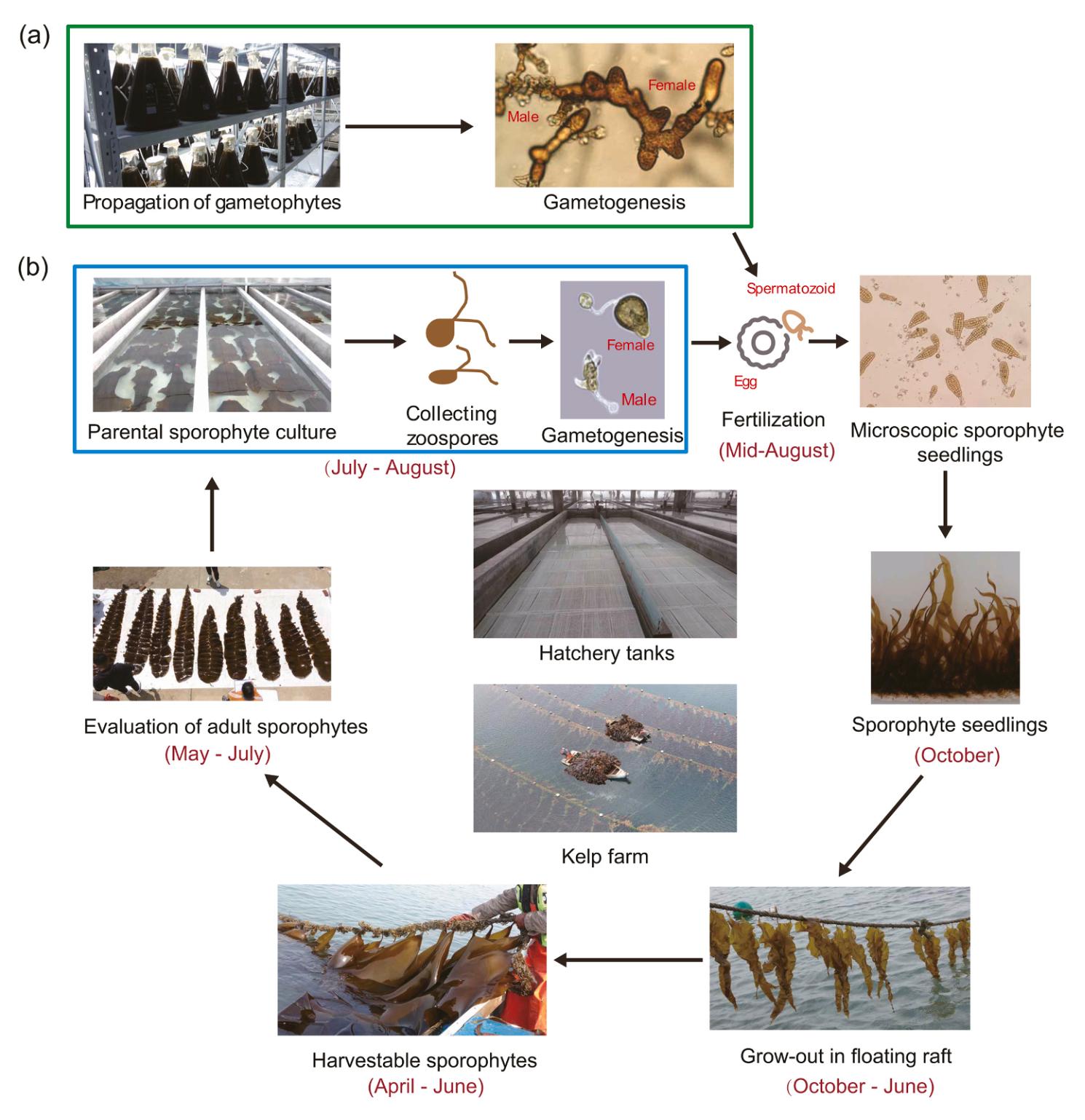 Full stage-covered Saccharina seedlings and cultivation production cycle in China. (Image by IOCAS)
Full stage-covered Saccharina seedlings and cultivation production cycle in China. (Image by IOCAS)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/earth/202506/t20250603_1044924.shtml
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S235251342500290X?via%3Dihub
コンブ養殖における遺伝的均質性の課題:10年後の中国からの考察 Challenges of genetic homogeneity in aquaculture of the kelp Saccharina japonica: Insights from China in ten year’s retrospect
Xiaodong Li (李晓东) , Lirong Chang (常丽荣) , Feng Han (韩枫) , Xia Li (李霞) , Luyang Xiao (肖露阳) , Ershuai Huang (黄二帅) , Yaning Yang (杨亚宁) , Li Su (苏丽) , Shaojun Pang (逄少军)
Aquaculture Reports Available online: 27 May 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2025.102904
Highlights
- Principal kelp cultivars in 2024 remain genetically homogeneous.
- Gene introgression has steadily changed the genetic compositions and structures.
- Hybridization using distinctly related germplasm improved productivity.
Abstract
Genetic homogeneity among principal cultivars of the kelp Saccharina japonica was first documented a decade ago in Rongcheng, a historically significant Saccharina farming city in China. Seven large-scale hatcheries in this region supply seedlings for approximately 50,795 ha of cultivation area, yielding ∼2.7 million metric tons of fresh biomass annually. These hatcheries have implemented independent breeding programs to enhance the productivity of cultivated populations. To assess decadal changes in farmed populations, we conducted a comprehensive investigation during the 2023–2024 cultivation cycle, combining microsatellite marker analysis of genetic composition/structure with open-sea cultivation trials to evaluate both genotypic and phenotypic characteristics. Our analyses confirmed persistent genetic homogeneity in five of six examined cultivars, consistent with prior findings. Standardized parental sporophyte selection criteria, coupled with uniform hatchery protocols and infrastructure, were identified as primary drivers of homogeneity. Notably, genetic introgression was detected in 2024 populations following the introduction of a hybrid cultivar developed through targeted hybridization at one hatchery. The incorporation of phylogenetically distinct germplasm induced measurable genotypic and phenotypic modifications in farmed populations, concomitant with productivity improvements. These findings underscore the necessity for hatcheries to maintain self-sustaining broodstock management and seedling production systems to preserve cultivar genetic integrity in a multi-hatchery operation environment. Regular monitoring of population genetic architecture is strongly recommended to ensure sustainable aquaculture practices.