2025-05-21 リンショーピング大学(LiU)
<関連情報>
- https://liu.se/en/news-item/major-step-for-flat-and-adjustable-optics
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-59764-5
スイッチング可能な狭い非局所導電性高分子プラズモニクス Switchable narrow nonlocal conducting polymer plasmonics
Dongqing Lin,Yulong Duan,Pravallika Bandaru,Pengli Li,Mohammad Shaad Ansari,Alexander Yu. Polyakov,Janna Wilhelmsen & Magnus P. Jonsson
Nature Communications Published:21 May 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-59764-5
Abstract
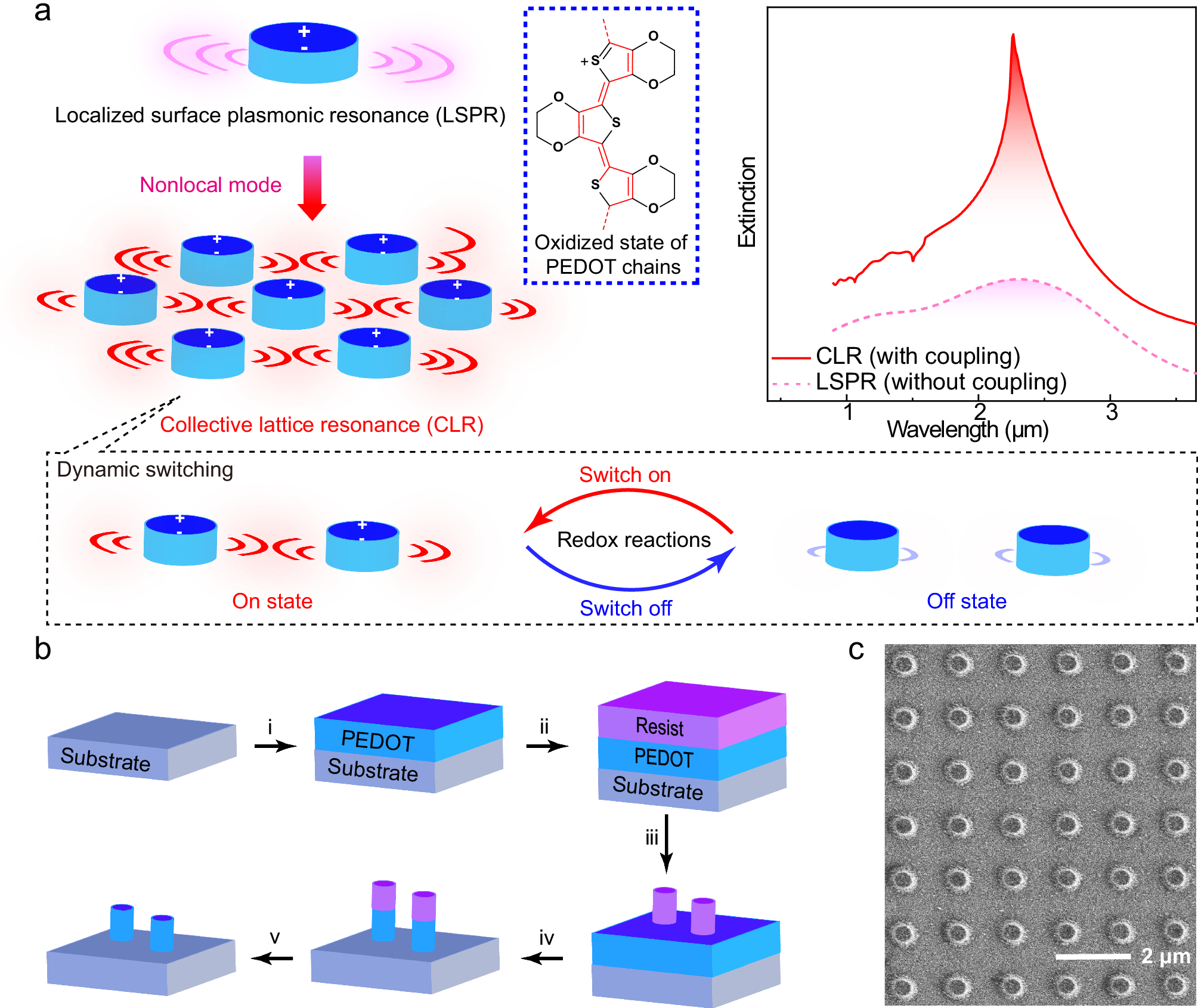
Dynamically switchable surface plasmons in conducting polymers constitute an emerging route towards intelligent metasurfaces, but polymer plasmons have so far suffered from weak resonances with low quality factors (Q < 1-2). Here, we address this by nonlocal coupling of individual poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) nanoantennas through collective lattice resonances (CLR) in periodic arrays (with resonance wavelengths around 2.0-4.5 μm). The results show that careful tuning of CLR matching conditions enables organic plasmonic resonances with Q up to 12. Angle-dependent extinction spectra connect the results to the enhancement of radiative coupling from diffractive lattice effects. Furthermore, the nonlocal coupling strength between nanoantenna units and lattice could be modulated via redox reactions, enabling the narrow CLRs to be reversibly switched with large modulation depth (between 7% and 45% extinction). By improving resonance strength and Q, the study circumvents previous limitations of conducting polymer plasmonics and shows feasibility for practical applications in active metasurfaces and nano-optics.