2025-05-13 京都大学
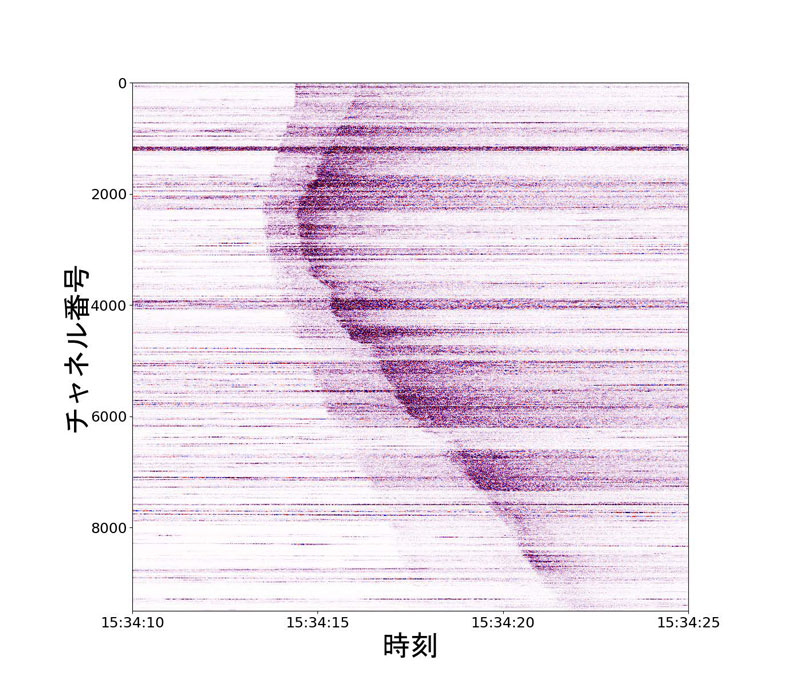
光ファイバーケーブルが捉えた小地震に伴う揺れの広がり
<関連情報>
- https://www.kyoto-u.ac.jp/ja/research-news/2025-05-13-0
- https://www.kyoto-u.ac.jp/sites/default/files/2025-05/web_2505_Miyazawa-00540deb21b2d4a54365660799e87167.pdf
- https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/2024GL113963
分散型音響センシング記録のS/P振幅比を用いた小規模地震の震源メカニズムの推定 Estimating Focal Mechanism of Small Earthquakes Using S/P Amplitude Ratios of Distributed Acoustic Sensing Records
Y. Funabiki, M. Miyazawa
Geophysical Research Letters Published: 03 May 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1029/2024GL113963
Abstract
We proposed a method for estimating focal mechanisms based on S/P amplitude ratios from distributed acoustic sensing (DAS) records for single earthquakes and successfully obtained the mechanisms from four events. This method involves measuring the maximum amplitude ratio between the S- and P-waves of the DAS records, followed by searching for the parameters of the focal mechanism. We applied this method to the DAS records of four shallow earthquakes from central Japan with magnitudes ranging from M2.2 to 3.4. The estimated mechanisms were consistent with the distribution of P-wave polarities from conventional seismometers despite recording only one component along the cable. This straightforward approach may be effective because of the wave scattering caused by near-surface heterogeneities and the varying orientations of the cable sections corresponding to the channels. Consequently, the observed scattered waves preserved the overall radiation patterns, allowing us to obtain the radiation patterns from a single-component record.
Key Points
- We estimated focal mechanisms using the S/P amplitude ratio from Distributed Acoustic Sensing records
- The estimated focal mechanisms were consistent with the initial polarity distribution from conventional seismograms
- This method can estimate the mechanism for a single event without correcting the cable geometry
Plain Language Summary
Understanding the focal mechanism of an earthquake, which indicates fault movement and geometry, is essential to understanding the earthquake process. We propose a method for estimating focal mechanisms using data from a novel fiber-optic sensing technique called distributed acoustic sensing (DAS). This technique allows a single fiber optic cable to operate similarly to thousands of seismograms. Our approach is based on the ratios of S-wave to P-wave amplitudes obtained from DAS records. This concept leverages the different radiation patterns of S-waves and P-waves. We used DAS data that recorded a series of small, shallow earthquakes in central Japan to estimate the source locations and focal mechanisms. The estimated mechanisms are consistent with those inferred from conventional seismograms. Moreover, the distribution of earthquakes and their focal mechanisms indicated that the sequence occurred along a left-lateral fault. Although the DAS measures only one component of the strain or strain rate along the cable, we were still able to successfully obtain the amplitude ratios of the S and P waves, which are typically orthogonal. This straightforward approach may work effectively because of the wave scattering caused by near-surface heterogeneities and the varying orientations of the cable sections corresponding to different channels.