2025-04-29 中国科学院(CAS)
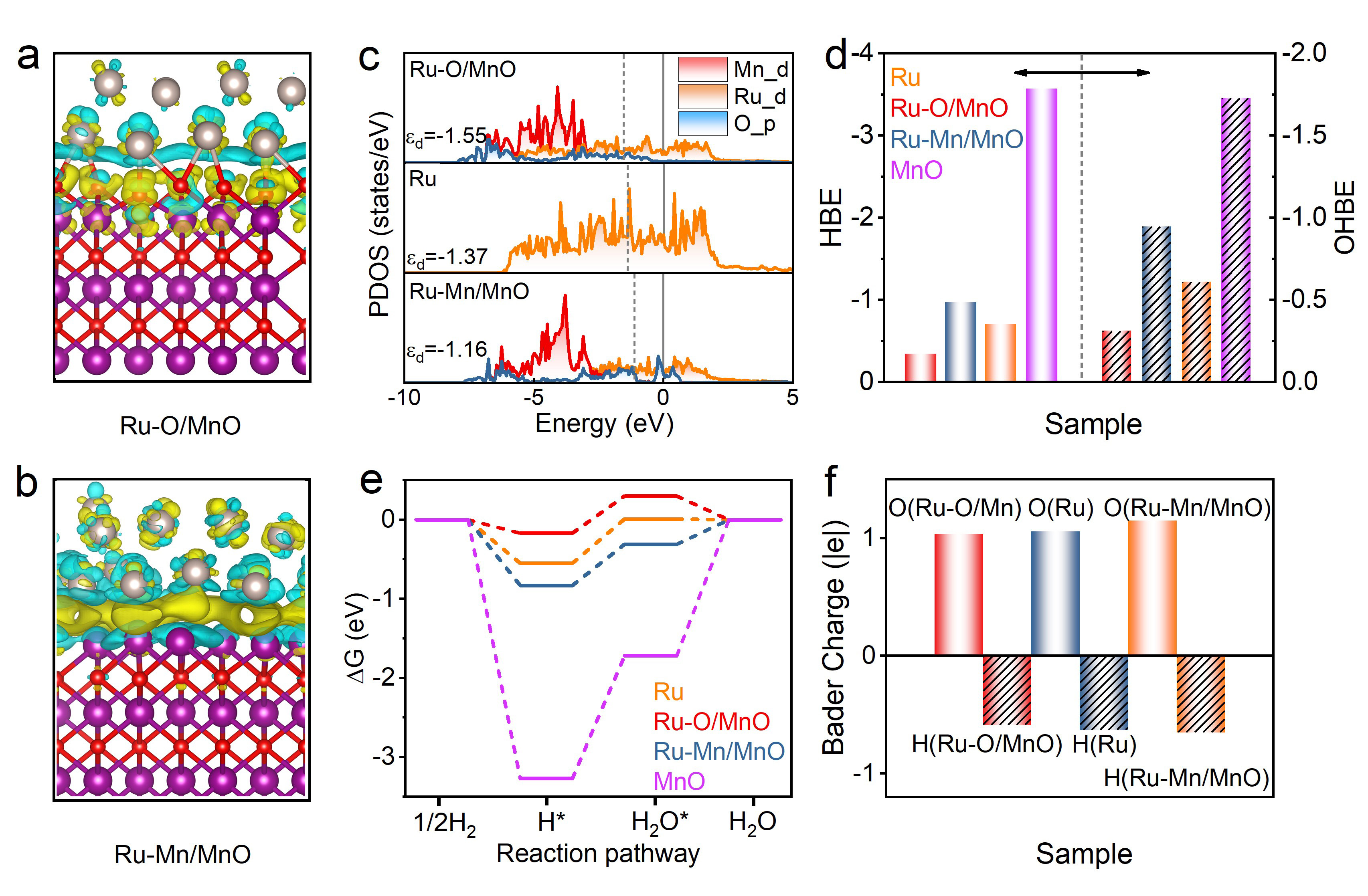 Theoretical calculation and modeling of the surface electronic structure of Ru catalysts and their HOR performance. (Image by ZHENG Fangcai)
Theoretical calculation and modeling of the surface electronic structure of Ru catalysts and their HOR performance. (Image by ZHENG Fangcai)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/phys/202504/t20250429_1042309.shtml
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.nanolett.4c06285
効率的なアルカリ水素酸化のための局所的な界面電子を最適化した格子閉じ込めルテニウム電極触媒 Lattice-Confined Ru Electrocatalysts with Optimal Localized Interfacial Electrons for Efficient Alkaline Hydrogen Oxidation
Xiaojuan Zhang,Zhiyuan Xia,Zhiqiang Li,Lingzhi Wei,Qiquan Luo,Fangcai Zheng,and Hui Wang
Nano Letters Published: March 6, 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.4c06285
Abstract
The interfacial electronic structure has a significant influence on the electrocatalytic activity and durability of metal oxide-supported ruthenium (Ru) electrocatalysts for the alkaline hydrogen oxidation reaction (HOR). Herein, we optimize the interfacial electronic structure by tuning the Ru–O bonds within MnO lattice-confined Ru electrocatalysts, creating efficient and stable sites for alkaline HOR. The formed Ru–O bonds generate localized interfacial electrons and a downshifted d-band center of interfacial Ru atoms, which results in optimal adsorption ability of H* and OH* together with the reduced energy barrier of H2O formation. The mass activity achieves 1.26 mA μgRu–1 in 0.1 M KOH, which is 13.0-fold and 8.0-fold higher than that of the contrast Ru/C (0.097 mA μgRu–1) and commercial Pt/C (0.158 mA μgPt–1), respectively, while also exhibiting favorable durability and CO tolerance. This work highlights the rational design of Ru–O bonds in optimizing the interfacial electronic structure to enhance the alkaline HOR activity.



