2025-03-20 理化学研究所,京都大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.riken.jp/press/2025/20250320_1/index.html
- https://www.kyoto-u.ac.jp/sites/default/files/2025-03/web_2503_Yanase-f1b2dadce2b7877a47a65ac8ad6515b7.pdf
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41567-025-02828-6
グラフェン上の単層NbSe2におけるねじれ角による超伝導の制御 Superconductivity controlled by twist angle in monolayer NbSe2 on graphene
Masahiro Naritsuka,Tadashi Machida,Shun Asano,Youichi Yanase & Tetsuo Hanaguri
Nature Physics Published:20 March 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41567-025-02828-6
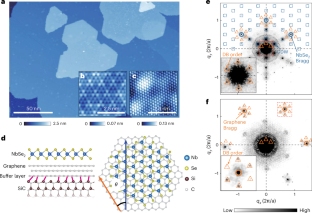
Abstract
Superconductivity serves as a basis for non-trivial quantum phenomena and devices, but they often require artificial control of the superconducting gap. In real space, there are various ways to tailor the superconducting gap, such as by introducing interfaces and defects. However, it is challenging to manipulate the superconducting gap in momentum space. Here we demonstrate that the superconducting gap of NbSe2 monolayers on graphene can be modified at specific momenta by changing the twist angle between the layers. Our spectroscopic-imaging-based scanning tunnelling microscopy experiments reveal the interference patterns of Bogoliubov quasiparticles that are twisted with respect to NbSe2 and graphene lattices. We find that these chiral interference patterns originate from the twist-dependent sextet of regions in momentum space in which the Fermi surfaces of the NbSe2 monolayer and graphene overlap. This finding not only broadens our understanding of superconductivity in twisted bilayer systems but also opens up possibilities for designing artificial superconducting materials and devices with tunable properties.



