2025-03-17 産業技術総合研究所
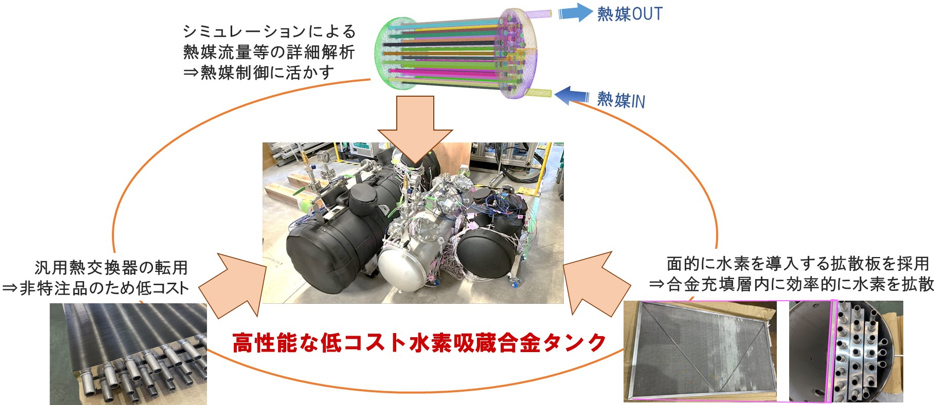 高性能な低コスト水素吸蔵合金タンクの開発概要図
高性能な低コスト水素吸蔵合金タンクの開発概要図
<関連情報>
- https://www.aist.go.jp/aist_j/press_release/pr2025/pr20250317/pr20250317.html
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0360319925007876
都市部でのオフサイト水素利用のための新しい熱媒体/水素流路を持つ高性能金属水素化物タンクの開発 Development of a high-performance metal hydride tank with novel heat-medium/hydrogen flow paths for off-site hydrogen use in urban areas
Yuta Segawa, Naruki Endo, Masahiko Okumura, Yasumasa Suzuki, Ryosuke Hayashi, Haruka Kitagawa, Toshihiro Yamane, Eisuke Shimoda
International Journal of Hydrogen Energy Available online: 1 March 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2025.02.216
Highlights
- TiFe-based MH tanks were developed with high performance <1 MPaG.
- The tank performed well even at 1/12.5 the flow velocity of heat exchanger design.
- Installation of a H2 diffuser plate improved performance by about 10%.
- A large MH tank with 88 Nm³ was developed and performed well.
- Obtained results could provide novel design guidelines for the MH tanks.
Abstract
In this study, we significantly enhanced the performance of metal hydride (MH) tanks without incurring substantial costs by adopting commercially available heat exchangers, optimizing heat-medium flow paths, and incorporating structures to improve hydrogen diffusibility. The significance of this study lies in the fabrication of a practically sized MH tank that achieves high hydrogen absorption and release performance below 1 MPaG, using commonly available heat exchangers and TiFe-based MH. Even when the flow velocity through the heat-medium path of the exchanger was low, optimizing the flow path design enabled excellent absorption and release performance. Furthermore, the adoption of an original hydrogen diffusion structure within the MH tank improved hydrogen diffusibility, thereby enhancing absorption and release performance. The developed tank demonstrated the hydrogen absorption and release capabilities required for off-site hydrogen utilization. The tank was also successfully scaled up to a size capable of storing approximately 88 Nm³ of hydrogen. The findings of this study are significant both academically and practically, and the integration of the fabricated tank into buildings has the potential to contribute substantially to the decarbonization of urban areas.