2025-02-25 中国科学院(CAS)
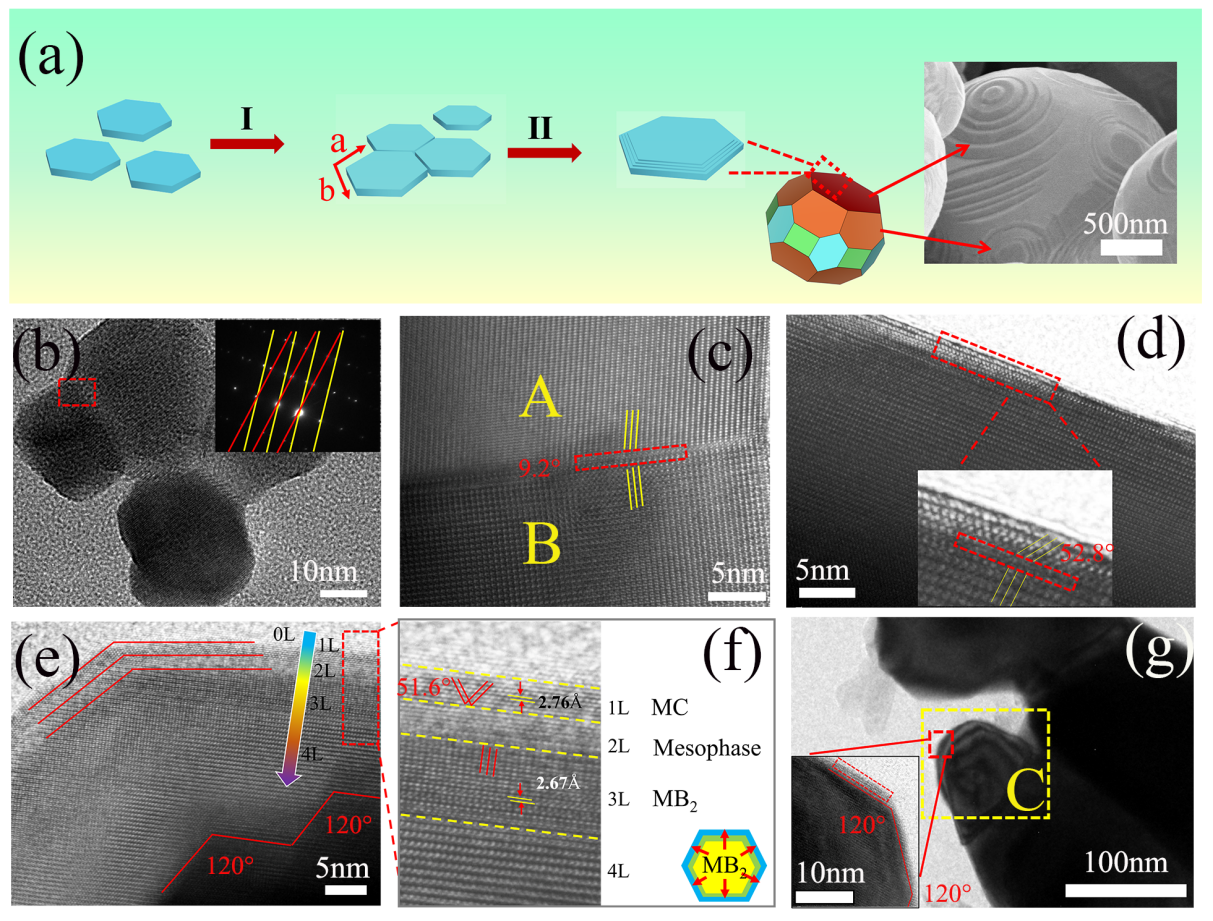 Boride Ceramic Particle Growth Process Schematic (Image by WANG Zhen)
Boride Ceramic Particle Growth Process Schematic (Image by WANG Zhen)
<関連情報>
- https://english.cas.cn/newsroom/research_news/phys/202502/t20250226_902634.shtml
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0955221925000718?via%3Dihub
高結晶性アルキメデス多面体(Zr0.5Hf0.5)B2ナノ粒子の成長機構と焼結特性 Growth mechanism and sintering properties of high crystallinity Archimedean polyhedral (Zr0.5Hf0.5)B2 nanoparticles
Zhen Wang, Yuan Cheng, Kewei Li, Mengen Hu, Hanwen Zhang Xian Dang, Ming Li, Xinyang Li, Zhulin Huang, Yue Li, Xiaoye Hu
Journal of the European Ceramic Society Available online: 31 January 2025
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2025.117251
Abstract
High quality ceramic powders are crucial for the performance of composite materials, yet preparing powders with good morphology and high crystallinity still faces enormous challenges. Herein we report a topological Archimedean polyhedron of (Zr0.5Hf0.5)B2 nanoparticles were synthesized via a high pressure liquid-phase and coprecipitation co-assisted boro/carbothermal reduction method. A nonclassical crystallization model where both oriented attachment and screw dislocation growth mechanism occur simultaneously. The microstructural evolution during the growth process of borides indicates that the growth mechanism of the new layer on the surface of diborides is mainly explained by the layered structure and trapezoidal profile. The initial growth stage energy of each layer comes from interface defects and lattice mismatches during atomic diffusion processes. The directional attachment of clusters leads to the generation of a large number of dislocations in the system, resulting in the formation of polyhedral structures. Benefiting from the high crystallinity polyhedral morphology, the powder shows excellent oxidation resistance, i.e., the thickness of ceramic oxide layer prepared by Archimedean polyhedron powders is 86.43 μm at 1400 °C for 3 h. This work holds significant importance for the development of new ceramic powders preparation methods and provides a novel approach for studying the performance improvement of ultra-high temperature ceramic materials.