2024-10-21 イリノイ大学アーバナ・シャンペーン校
<関連情報>
- https://aces.illinois.edu/news/study-combines-woodchips-and-biochar-clean-water-pharmaceuticals-nutrients
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304389424024610
二段式ウッドチップ・バイオリアクター・バイオチャール処理システムによる栄養素と医薬品・パーソナルケア製品の同時除去 Simultaneous removal of nutrients and pharmaceuticals and personal care products using two-stage woodchip bioreactor-biochar treatment systems
Hongxu Zhou, Haribansha Timalsina, Shuai Tang, Sophie Circenis, Jason Kandume, Richard Cooke, Buchun Si, Rabin Bhattarai, Wei Zheng
Journal of Hazardous Materials Available online: 17 September 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2024.135882
Graphical Abstract

Highlights
- The woodchip bioreactor – biochar treatment systems removed nutrients and PPCPs.
- Longer HRTs and smaller biochar particle size enhanced the pollutant removal.
- Biochar systems mitigated by-product leaching from woodchip bioreactor.
- PPCPs led to microorganism changes in the woodchip bioreactor.
- Strategy was proposed to guide the engineering application of the treatment system.
Abstract
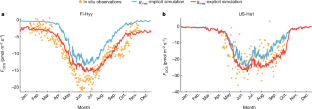
The co-occurrence of nutrients and pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in sewage effluent can degrade water quality of the receiving watersheds. This study investigated the simultaneous removal of excess nutrients and PPCP contaminants by developing a novel woodchip bioreactor and biochar (B2) treatment system. The result revealed that woodchip bioreactors could effectively remove nitrate via a denitrification process and adsorb some PPCPs. Biochar as a secondary treatment system significantly reduced the concentrations of PPCPs and dissolved reactive phosphorus (DRP) (p < 0.05), compared to the woodchip bioreactor. The removal efficiencies of all targeted contaminants by the B2 system were evaluated using various hydraulic retention times (HRTs) and biochar types (pelletized versus granular biochar). Longer HRTs and smaller biochar particles (granular biochar) could enhance the removal efficiencies of targeted contaminants. Average contaminant removals were 77.25 % for nitrate-N, 99.03 % for DRP, 69.51 % for ibuprofen, 73.65 % for naproxen, 91.09 % for sitagliptin, and 96.96 % for estrone, with woodchip bioreactor HRTs of 12 ± 1.4 h and granular biochar HRTs of 2.1 ± 0.1 h. Notably, the second-stage biochar systems effectively mitigated by-products leaching from woodchip bioreactors. The presence of PPCPs in the woodchip bioreactors enriched certain species, such as Methylophilus (69.6 %), while inhibiting other microorganisms and reducing microbial community diversity. Furthermore, a scaled-up B2 system was analyzed and assessed, indicating that the proposed engineering treatment system could provide decades of service in real-world applications. Overall, this study suggests that the B2 system has promising applications for addressing emerging and conventional contaminants.