2024-05-08 オランダ・デルフト工科大学(TUDelft)
<関連情報>
- https://www.tudelft.nl/en/2024/tnw/disorder-improves-battery-life
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-024-07362-8
酸化リチウム正極における化学的短距離乱れ Chemical short-range disorder in lithium oxide cathodes
Qidi Wang,Zhenpeng Yao,Jianlin Wang,Hao Guo,Chao Li,Dong Zhou,Xuedong Bai,Hong Li,Baohua Li,Marnix Wagemaker & Chenglong Zhao
Nature Published:08 May 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07362-8
Abstract
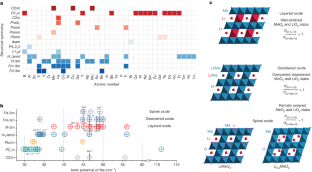
Ordered layered structures serve as essential components in lithium (Li)-ion cathodes. However, on charging, the inherently delicate Li-deficient frameworks become vulnerable to lattice strain and structural and/or chemo-mechanical degradation, resulting in rapid capacity deterioration and thus short battery life. Here we report an approach that addresses these issues using the integration of chemical short-range disorder (CSRD) into oxide cathodes, which involves the localized distribution of elements in a crystalline lattice over spatial dimensions, spanning a few nearest-neighbour spacings. This is guided by fundamental principles of structural chemistry and achieved through an improved ceramic synthesis process. To demonstrate its viability, we showcase how the introduction of CSRD substantially affects the crystal structure of layered Li cobalt oxide cathodes. This is manifested in the transition metal environment and its interactions with oxygen, effectively preventing detrimental sliding of crystal slabs and structural deterioration during Li removal. Meanwhile, it affects the electronic structure, leading to improved electronic conductivity. These attributes are highly beneficial for Li-ion storage capabilities, markedly improving cycle life and rate capability. Moreover, we find that CSRD can be introduced in additional layered oxide materials through improved chemical co-doping, further illustrating its potential to enhance structural and electrochemical stability. These findings open up new avenues for the design of oxide cathodes, offering insights into the effects of CSRD on the crystal and electronic structure of advanced functional materials.