2024-05-20 ペンシルベニア州立大学(PennState)
<関連情報>
- https://www.psu.edu/news/engineering/story/shining-light-molecules-l-shaped-metamaterials-can-control-light-direction/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-48051-4
L型誘電体メタマテリアルで広帯域増強光のキラリティを制御する Controlling the broadband enhanced light chirality with L-shaped dielectric metamaterials
Ufuk Kilic,Matthew Hilfiker,Shawn Wimer,Alexander Ruder,Eva Schubert,Mathias Schubert & Christos Argyropoulos
Nature Communications Published04 May 2024
DOIhttps://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-48051-4
Abstract
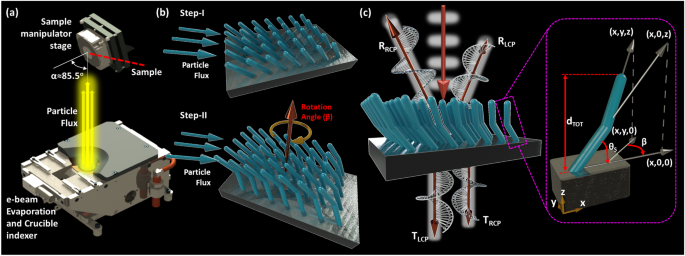
The inherently weak chiroptical responses of natural materials limit their usage for controlling and enhancing chiral light-matter interactions. Recently, several nanostructures with subwavelength scale dimensions were demonstrated, mainly due to the advent of nanofabrication technologies, as a potential alternative to efficiently enhance chirality. However, the intrinsic lossy nature of metals and the inherent narrowband response of dielectric planar thin films or metasurface structures pose severe limitations toward the practical realization of broadband and tailorable chiral systems. Here, we tackle these problems by designing all-dielectric silicon-based L-shaped optical metamaterials based on tilted nanopillars that exhibit broadband and enhanced chiroptical response in transmission operation. We use an emerging bottom-up fabrication approach, named glancing angle deposition, to assemble these dielectric metamaterials on a wafer scale. The reported strong chirality and optical anisotropic properties are controllable in terms of both amplitude and operating frequency by simply varying the shape and dimensions of the nanopillars. The presented nanostructures can be used in a plethora of emerging nanophotonic applications, such as chiral sensors, polarization filters, and spin-locked nanowaveguides.