2024-03-19 ブラウン大学
<関連情報>
- https://www.brown.edu/news/2024-03-19/salt-sized-sensors
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41928-024-01134-y
自律型センサーの大規模集団からイベント駆動型データを取得するための非同期無線ネットワーク An asynchronous wireless network for capturing event-driven data from large populations of autonomous sensors
Jihun Lee,Ah-Hyoung Lee,Vincent Leung,Farah Laiwalla,Miguel Angel Lopez-Gordo,Lawrence Larson & Arto Nurmikko
Nature Electronics Published:19 March 2024
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-024-01134-y
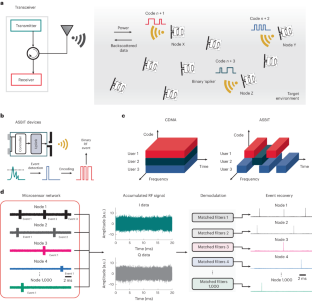
Abstract
Networks of spatially distributed radiofrequency identification sensors could be used to collect data in wearable or implantable biomedical applications. However, the development of scalable networks remains challenging. Here we report a wireless radiofrequency network approach that can capture sparse event-driven data from large populations of spatially distributed autonomous microsensors. We use a spectrally efficient, low-error-rate asynchronous networking concept based on a code-division multiple-access method. We experimentally demonstrate the network performance of several dozen submillimetre-sized silicon microchips and complement this with large-scale in silico simulations. To test the notion that spike-based wireless communication can be matched with downstream sensor population analysis by neuromorphic computing techniques, we use a spiking neural network machine learning model to decode prerecorded open source data from eight thousand spiking neurons in the primate cortex for accurate prediction of hand movement in a cursor control task.