2023-12-20 カリフォルニア大学リバーサイド校(UCR)
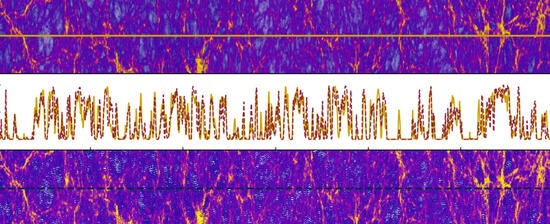
TACC’s Frontera supercomputer helped astronomers develop PRIYA, the largest suite of hydrodynamic simulations yet made of large-scale structure in the universe. Image shows Lyman-α forest spectra from quasar light and corresponding gas density and temperature from simulations at redshift z = 4. Top panel shows high resolution, bottom panel shows low resolution, middle panel shows the Lyman-α forest spectra. (DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2309.03943)
◆UCリバーサイドのSimeon Bird博士が率いるプロジェクトでは、クェーサーの光がビッグバン後の中性水素ガス雲を透過し、宇宙の大規模構造に関する手がかりを提供する新しいシミュレーションモデルを構築。PRIYAはeBOSSからの光データを使用し、異なる宇宙論的パラメーターと初期条件でのシミュレーションモデルと比較して宇宙の物質と構造の量を評価。
<関連情報>
- https://news.ucr.edu/articles/2023/12/20/supercomputer-enables-illustration-large-scale-structure-universe
- https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1475-7516/2023/10/037
- https://arxiv.org/abs/2309.03943
PRIYA:宇宙論のための新しいライマンαフォレストシミュレーション群 PRIYA: a new suite of Lyman-α forest simulations for cosmology
Simeon Bird, Martin Fernandez, Ming-Feng Ho, Mahdi Qezlou, Reza Monadi, Yueying Ni, Nianyi Chen, Rupert Croft and Tiziana Di Matteo
Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics Published 11 October 2023
DOI:10.1088/1475-7516/2023/10/037
Abstract
We present the PRIYA suite of cosmological simulations, based on the code and hydrodynamic model of the ASTRID simulation, and designed for cosmological analyses of the Lyman-α forest. Our simulation suite spans a 9-dimensional parameter space, including 4 cosmological parameters and 5 astrophysical/thermal parameters. We have run 48 low fidelity simulations with 15363 particles in a 120 Mpc/h box and 3 high fidelity simulations with 30723 particles in a 120 Mpc/h box. All our simulations include a full physics model for galaxy formation, including supernova and AGN feedback, and thus also contain a realistic population of DLAs. We advance on earlier simulations suites by larger particle loads, by incorporating new physical models for patchy hydrogen and helium reionization, and by self-consistently incorporating a model for AGN feedback. We show that patchy helium reionization imprints an excess in the 1D flux power spectrum on large scales, which may allow future measurements of helium reionization bubble sizes. Simulation parameters are chosen based on a Latin hypercube design and a Gaussian process is used to interpolate to arbitrary parameter combinations. We build a multi-fidelity emulator for the 1D flux power spectrum and the mean IGM temperature. We show that our final interpolation error is < 1% and that our simulations produce a flux power spectrum converged at the percent level for z = 5.4–2.2. Our simulation suite will be used to interpret Lyman-α forest 1D flux power spectra from SDSS and future DESI data releases.
PRIYAシミュレーションによるeBOSSライマンαの森からの宇宙論的制約 Cosmological Constraints from the eBOSS Lyman-α Forest using the PRIYA Simulations
M.A. Fernandez, Simeon Bird, Ming-Feng Ho
arXiv Submitted on 7 Sep 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2309.03943
We present new cosmological parameter constraints from the eBOSS Lyman-α forest survey. We use a new theoretical model and likelihood based on the PRIYA simulation suite. PRIYA is the first suite to resolve the Lyman-α forest in a (120 Mpc/h)3 volume, using a multi-fidelity emulation technique. We use PRIYA to predict Lyman-α forest observables with ≲1% interpolation error over an 11 dimensional (9 simulated, 2 in post-processing) parameter space. We identify an internal tension within the flux power spectrum data. Once the discrepant data is removed, we find the scalar spectral index at k=0.78 h/Mpc to be np=0.97−0.995 at 68% confidence from the Lyman-α forest flux power spectrum alone, in good agreement with Planck. The amplitude of matter fluctuations is σ8=0.733±0.026 at 68% confidence, in agreement with Dark Energy Survey weak lensing measurements and other small-scale structure probes and in tension with CMB measurements from Planck and ACT. The effective optical depth to Lyman-α photons from our pipeline is in good agreement with earlier measurements. We add measurements of the mean temperature of the intergalactic gas from z=3.8−2.2 and use them to constrain the duration and heating rate of helium reionization, finding a preference for an early, hot, helium reionization event, as suggested by measurements from the helium Lyman-α forest. Adding the mean IGM temperature data also increases the significance of the σ8 tension. In the near future we will use our pipeline to infer cosmological parameters from the DESI Lyman-α data.



