2023-11-20 NASA
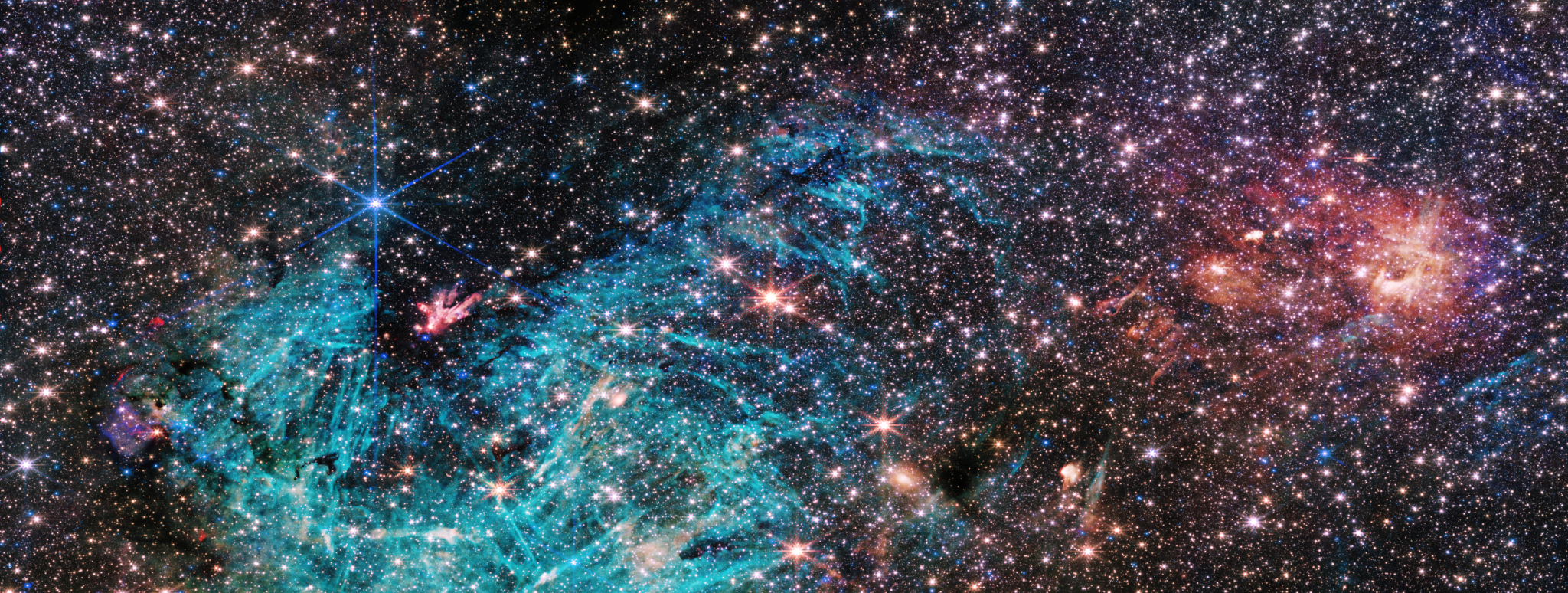

The NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera) instrument on NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope’s reveals a portion of the Milky Way’s dense core in a new light. An estimated 500,000 stars shine in this image of the Sagittarius C (Sgr C) region, along with some as-yet unidentified features. A large region of ionized hydrogen, shown in cyan, contains intriguing needle-like structures that lack any uniform orientation.
NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, and S. Crowe (University of Virginia).
◆ウェッブ宇宙望遠鏡が銀河中心の観測データを提供し、これまでにない詳細な星形成の特徴を明らかにしました。画像には形成中のプロトスターのクラスターや赤外線暗黒雲が含まれ、ウェッブの高感度が密集した領域を捉えました。
◆特に驚きのデータには、大質量のプロトスターが放射するイオン化水素の広がりがあり、これがさらなる研究を促しています。銀河中心は乱雑で活気に満ちた場所であり、形成中の星が周囲のガスに与える影響も明らかになっています。最終的に、ウェッブのデータは宇宙の起源に関する新たな洞察を提供し、特に大質量の星が宇宙の元素を生み出す過程を理解する上で重要な情報源となっています。
<関連情報>