2023-0906 スイス連邦工科大学ローアン校(EPFL)
特に、低電圧で動作する電界効果トランジスタ(TFET)が注目され、デバイスの消費電力を大幅に削減する可能性があります。この技術は、電子デバイスの性能向上と新たな応用分野を開拓する可能性があります。
<関連情報>
- https://actu.epfl.ch/news/analog-digital-best-of-both-worlds-in-one-energy-e/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41928-023-01018-7
急勾配ロジックとニューロモルフィックデバイスの統合のための2次元半導体の強誘電体ゲーティング Ferroelectric gating of two-dimensional semiconductors for the integration of steep-slope logic and neuromorphic devices
Sadegh Kamaei,Xia Liu,Ali Saeidi,Yingfen Wei,Carlotta Gastaldi,Juergen Brugger & Adrian M. Ionescu
Nature Electronics Published:31 August 2023
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-023-01018-7
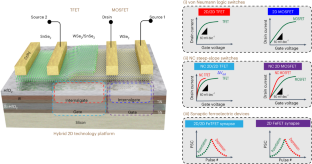
Abstract
The co-integration of logic switches and neuromorphic functions could be used to create new computing architectures with low power consumption and novel functionalities. Two-dimensional (2D) semiconductors and ferroelectric materials could be potentially used to make such devices, but integrating them on the same platform is challenging. Here we show that the 2D semiconductor tungsten diselenide and 2D/2D heterostructures of tungsten diselenide/tin diselenide can be integrated with doped high-k ferroelectric (silicon-doped hafnium oxide) and high-k dielectric gate stacks. With this single platform, four types of logic switch—2D metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors (FETs), 2D/2D tunnel FETs, negative-capacitance 2D FETs and negative-capacitance 2D/2D tunnel FETs—can be created. The negative-capacitance tungsten diselenide/tin diselenide tunnel FET exhibits an average subthreshold swing of 55 mV dec–1 over four decades of current, and the negative-capacitance tungsten diselenide FET exhibits an average subthreshold swing of 50 mV dec–1 over three decades. The shared ferroelectric gate stacks on 2D devices can also be exploited to create co-integrated artificial synapses for neuromorphic computing.